By Sherry Bunting, Farmshine, June 7, 2024
USDA announced new actions and $824 million in emergency funding from the Commodity Credit Corporation (CCC) to focus on highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) known as Bovine Influenza A in dairy cattle, which is the H5N1 virus.
Call it what you will, these funds target HPAI in dairy cattle through data collection, surveillance, diagnostics, as well as vaccine research, and food safety studies to better understand and mitigate outbreak risk.
In the May 31 announcement, USDA also launched a new Voluntary H5N1 Dairy Herd Status Pilot Program to monitor the health of dairy herds and allow enrolled farms to move cows more quickly, while providing on-going testing that would expand USDA’s herd surveillance capabilities.
Dairy farms that enroll in the recently announced voluntary monitoring program would sign Herd Monitoring Plan Agreements to do weekly bulk tank testing, enabling them to move dairy cows across state lines without doing the individual pre-movement testing – as long as their weekly bulk tank tests show three consecutive weeks of negative results, and as long as they agree to continue the tests weekly going forward.
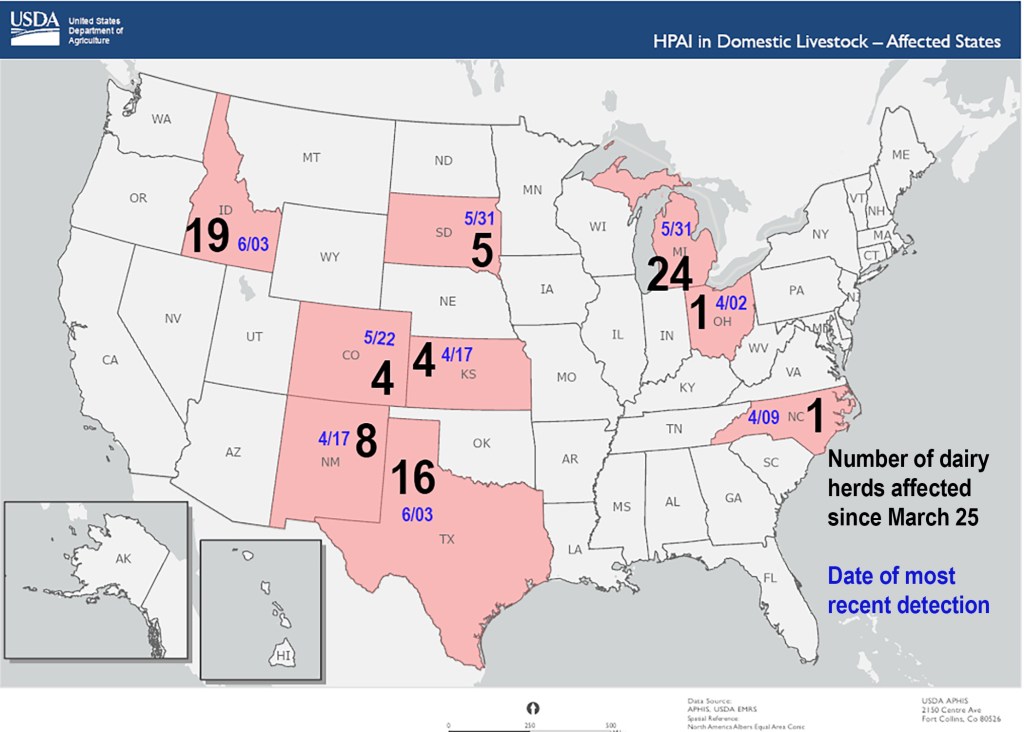
As of June 5, 2024, the APHIS website shows 82 total HPAI detections in dairy herds in 9 states since the first detection in Texas on March 25.
Topping the list is Michigan with 24 detections, the most recent on May 31. Idaho saw a slew of new detections over the past 10 days with 19 total, the most recent on June 3. Texas has had 16 detections, the most recent on June 3; followed by South Dakota with 5 detections, the most recent May 31; and Colorado with 4, the most recent May 22.
States that have seen no new detections since April include New Mexico (8) and Kansas (4) with their last new detections on April 17; Ohio and North Carolina each only had one dairy herd detection on April 2 and April 9, respectively.
According to USDA, the new voluntary monitoring program will enable the Department to increase its monitoring and surveillance of herds that are currently not known to be infected.
APHIS is working with state animal health officials to identify states that want to participate in a pilot phase of the program. Producers from participating states can start enrolling this week (June 3), by contacting their State Veterinarian and signing a Herd Monitoring Plan Agreement.
USDA says high participation will help them establish state and/or regional “disease-free statuses” that could further ease compliance with the current Federal Order.
Those herds not enrolled in the pilot program would continue to follow the interstate testing and movement requirements published in the Federal Order. More specific guidance on the new voluntary monitoring program, including how to enroll and how to obtain and maintain a herd status, will be made available on the APHIS website in the future or by contacting state animal health officials.
USDA expects to see increased testing, yielding increased positive detections, through this voluntary monitoring, which they will analyze to learn how HPAI may spread between herds.
To-date, three people who worked with infected cows (two in Michigan and one in Texas) have tested positive with the H5N1 influenza. The symptoms were similar to pinkeye, and they recovered in a few days.
Meanwhile, the Federal Government has already put $200 million in additional funds into surveillance, testing, PPE, and vaccine development with indications they will ask Congress for more ‘bird flu’ funding.
Authorities still deem the risk to the general public as very low because pasteurization deactivates the virus, and no detections have been found in any retail meat samples. In addition, milk from sick cows is discarded and cattle at beef plants are inspected.
The $824 million will also support anticipated diagnostics, field response, other necessary surveillance and control, surveillance in wildlife (APHIS), work by the Agricultural Research Service’s (ARS) in developing vaccines for HPAI in cattle, turkeys, pigs, and goats, and food safety studies conducted by ARS and the Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS).
The Secretary is authorized to transfer funding from available resources including the CCC to address emergency outbreaks of animal and plant pests and diseases. The new $824 million is focused primarily on dairy cattle in addition to previously approved $1.3 billion in emergency funding to address nationwide HPAI detections in wild birds and commercial poultry operations.
More information is available at the designated APHIS page at https://www.aphis.usda.gov/livestock-poultry-disease/avian/avian-influenza/hpai-detections/livestock
States are moving to issue their own additional emergency response plans. In Pennsylvania, for example, the Department of Agriculture recently issued its General Quarantine Order for the Exhibition of Dairy Cattle, which would apply to all dairy cows traveling to shows and exhibitions. This would ONLY take effect IF a detection is confirmed anywhere in the state. It would apply to all dairy cows traveling to shows and exhibitions.
If that happens, the Order would require testing through the PADLS system within 7 days of the date of arrival at any animal exhibition grounds. Prior to arrival those dairy cows would have to be part of a biosecure assembled group for 30 days prior to testing with no new cattle added to that assembly.
Other quarantine measures are also detailed in the Pennsylvania Order, but again, would only be implemented IF HPAI is detected in dairy cattle in Pennsylvania.
The Center for Dairy Excellence will have its monthly conference call on the subject June 12 at 1:00 p.m. For information, go to the special events page at https://www.centerfordairyexcellence.org/about-the-center/upcoming-events/event/weekly-hpai-calls/
