By Sherry Bunting, Farmshine, Feb. 16, 2024
EAST EARL, Pa. — While decades of scientific debate in terms of childhood health and nutrition is the curtain opponents hide behind, the anti-animal agenda is the top hurdle for the Whole Milk for Healthy Kids Act in the Senate.
Senator Roger Marshall (R-Kan.) is the prime sponsor of the Senate bill, and he is a medical doctor in obstetrics and is taking a beating from billboards sponsored by Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine (PCRM) in his home state of Kansas. PCRM is a known arm of PETA. This tells us quite a bit, doesn’t it?
Meanwhile, the top 3 C’s facing the bill within the dairy industry, itself, need to be addressed.
1) Confusion… Will it really improve milk prices? Addressed in this article
2) Consternation (fear)… What will processors do with “all of that skim”? Addressed in Part II here
3) Competition… Will it reduce the butterfat supply and affect the ramp up in cheese manufacturing or other dairy products? Addressed in Part III here
Plus…. the Checkoff Commitments… Will it interfere with checkoff-funded Milk Molecules Initiative for new beverages that identify and separate specific milk molecules for specific benefits (sleep drinks, energy drinks, immune function drinks, specific protein type drinks)?
All of these questions are quietly floating around and sowing seeds of doubt, leading to analysis-paralysis, while the industry focus is on innovation and exports, not on fresh milk, or a healthy next generation of U.S. milk consumers.
All of these questions will be answered one at a time over the next several weeks, starting with the first “C”: Confusion.
“Will this bill really improve our milk prices?” was the question I was asked by a few farmers at a recent farm show. My response was to ask them if they are concerned about kids having healthy milk options they enjoy and if they are concerned about seeing further erosion of fluid milk sales, and losing another generation of milk drinkers?
I reached out to Calvin Covington, former milk cooperative CEO in the fluid milk markets of the Southeast and a primary architect of pricing milk by component yield even before Order Reform during his years with American Jersey Cattle Breeders.
Covington ran the numbers using 2023 average prices, and calculating pounds of milk, fat, and skim, utilization, and values, which yield a gross value of a hundredweight of milk being used for fluid processing at different fat levels.
“At a $3.00 Class I differential, a hundredweight of milk going for 3.25 fluid milk (whole milk as standardized), returns an additional 25 cents per hundredweight over skim milk,” Covington writes, noting that the difference will change based on different Class I differentials.
Even in the counties with small or zero location differentials on the map, the base differential of $1.60 per hundredweight is still included, which means at least a 13 cents per hundredweight difference.
Previously, Covington has noted in presentations that milk prices improve as the average fat level of total fluid milk sales increases. The current average of all sales, nationwide, stands at 2%. A few years ago, it was below 2%. A fractional change in either direction influences Federal Milk Marketing Order blend prices.
Fluid milk demand also plays a role in manufacturing class prices, affecting farmers in regions where prices are based almost exclusively on cheese.
That’s especially true right now as cheese production has been exploding, and the Class III milk price has been imploding, creating a wide spread below Class IV and pushing FMMO blend prices lower as milk is not moving out of Class III to the higher value Class IV. But the Federal Milk Marketing Law gives Class I dibs to attract milk. So Class I demand is relevant for cheese milk pricing too.
As whole milk sales have increased year-over-year, whole milk became the largest category of fluid milk sales in 2021. It is a bright spot in the fluid milk category.
In 2023, gains in whole milk sales and in lactose-free milk sales are credited with boosting the entire fluid milk category for year-over-year gains in back-to-back months of October and November. This helped flatten the year-to-date loss-curve on total fluid milk sales that had been running 2 to 4% lower year-over-year to be just 1.5% lower cumulatively at year end compared with 2022, according to USDA’s December estimated packaged fluid milk sales report, released in mid-February.
Still, there is ground to make up, as fluid milk sales volume in 2023 is 7.8% lower than pre-Covid 2019, when volume totaled 46.24 billion pounds, down 1.8% from 2018. Then, during pandemic lockdowns, milk sales stabilized, putting the total at 46.2 billion pounds for 2020, virtually unchanged from 2019. In 2021, fluid milk sales volume declined 4.1% to 44.3 billion pounds, followed by a 2.4% decrease in 2022 to 43.3 billion pounds, and now a 1.5% decline in 2023 at 42.6 billion pounds.
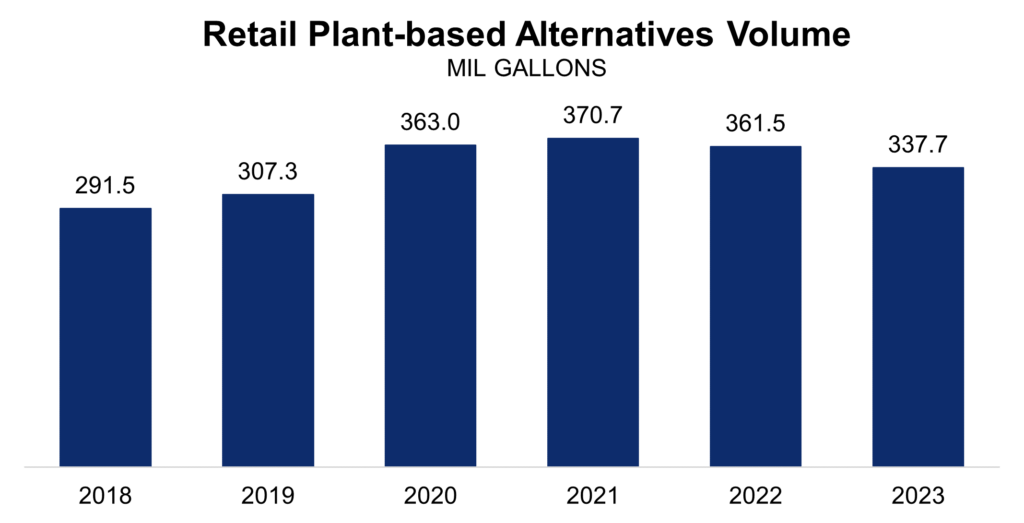
Meanwhile, the big news reported recently is that plant-based fake-milk beverages saw sales decline by 6.6% in 2023, the second straight year of declines and the smallest sales since 2019, according to data from Circana Inc reported recently.
Real dairy milk sales volume of 42.6 billion pounds in 2023 is not only a much larger category than the lookalikes at 337.7 million pounds, real dairy milk outperformed lookalikes on a trend basis in 2023 — down just 1.5% vs. plant-based being down 6.6%.
By comparison, plant-based beverage sales volume in 2023 was a fraction of 1% (0.8%) the size of real milk sales volume.
Whole milk education and awareness have helped drive this result. Consumers are paying attention to food science, even if the Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee, USDA (and FDA on labeling) continue to ignore it. Still, more education and freedom for children to enjoy milk is needed. The concern is that even though it is a smaller percentage loss, the 1.5% sales volume loss in the real milk category in 2023 represented 644 million pounds; whereas a 6.6% sales volume loss in plant-based beverages in 2023 represented 24 million pounds.
Speaking with a local milk bottler and ice cream maker recently – a producer handler – I learned he focuses on how his cows are fed to maintain their rolling average 5% butterfat during the summertime to make ice cream and satisfy consumer demand for whole milk. Their whole milk sales have skyrocketed, and this in turn, to the delight of the grocery store they are in, has helped boost sales of all fluid milk as a category in that store.
This has him thinking of doing a 5% butterfat, non-standardized, maybe even cream top, full-fat milk in glass bottles for the store. The store displays a 97 Milk banner at the entrance and 97milk.com website stickers at the dairy case.
Speaking with a manager at a different grocery store chain with stores in Pennsylvania and surrounding states, I learned their sales of whole milk have also increased by leaps and bounds in the past several years, boosting the entire fluid milk category by 14% at their stores throughout the region. They include the 97milk.com website and information in their sales circulars to their shoppers.
As for the schools — If even half of the schools offered a mix of milkfat choices as the Whole Milk for Healthy Kids Act would allow them to do, the amount of butterfat sold as Class I would increase. This would improve the fat side of the fat/skim pricing in the three Southeast Orders and Arizona. It would also help the Federal Order pool dollars reach after actual components are paid first in Multiple Component Pricing Orders everywhere else.
Total Class I fluid milk sales have dropped like a rock since Congress passed the Healthy Hunger Free Kids Act in 2010, which removed whole and 2% milk options from school meals, followed by USDA in 2012 further banning whole and 2% milk as a la carte or vending machine ‘competing beverage’ options in the Department’s Smart Snacks regulations.
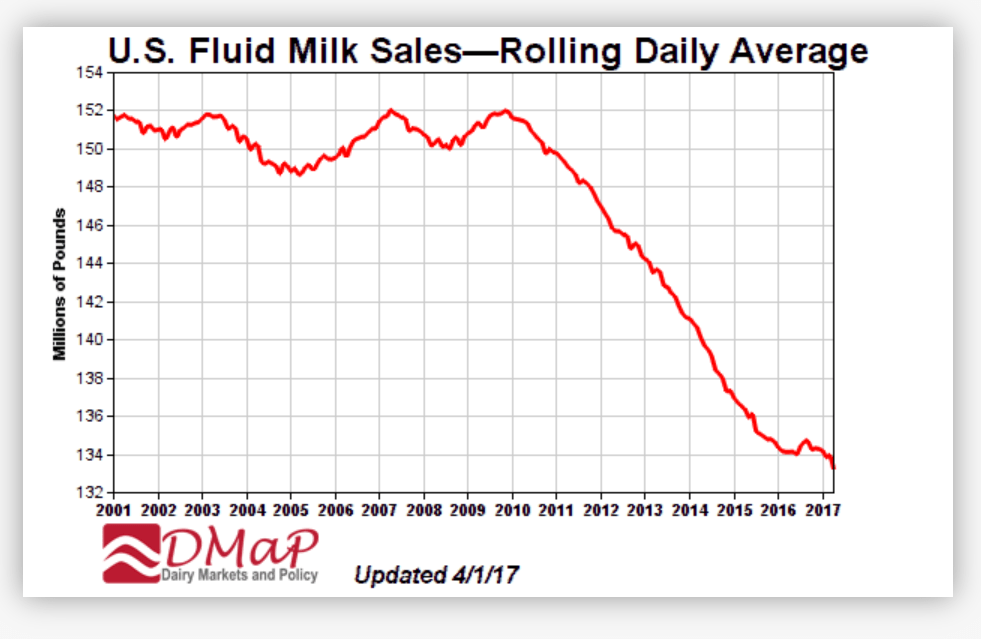
Look at the graph above. It was shared as part of Dr. Mark Stephenson’s testimony in the recent USDA FMMO milk pricing hearing.
Improved total sales of school milk hold potential to increase total Class I fluid milk sales. A Pennsylvania school trial in 2019 showed a 52% increase in milk sales when whole and 2% milk options were offered. Students showed a 3 to 1 preference for whole milk over the 1% milk option.
When their options were expanded, more students chose milk instead of refusing it. Students were able to choose, and some of them continued to choose low-fat, and that’s okay! The Whole Milk for Healthy Kids Act is about choice.
A conservative estimate of a 25% increase in school milk sales can be anticipated if Whole Milk for Healthy Kids gets over the finish line in the Senate after its overwhelming passage in December in the House. That is half of the increase seen in the Pennsylvania school trial. If realized, a 25% increase in school milk sales equates to a little over one billion pounds of additional annual milk sales, which could raise the entire Class I fluid milk category by a little more than 2%.
This is based on the fact that kids aren’t just throwing away milk at school. Some are refusing to take the milk they are offered with school meals. This means sales are being lost.
Fluid milk sales declines will only get worse if USDA implements one of two draft proposals the Department announced a year ago. One would eliminate flavored milk from elementary and middle schools altogether. The other would require added sugar levels to be reduced dramatically in flavored milk at school. It’s widely known that when milkfat is retained in making chocolate milk, less added sugar is needed!
Demand for whole milk is beneficial on both the milk fat and skim sides of the equation because whole milk sales move the nearly-complete product – the skim with the fat — leaving some of the fat through standardization, but not leaving any skim.
The result of these options in schools could be even better depending on how many schools choose to exercise these options.
If the industry doesn’t supply what consumers demand, sales are lost. Schoolchildren are already the dairy industry’s consumers, and they will hold the purse strings in the future.
Just as the Dietary Guidelines Committee and USDA continue to ignore science on milkfat, we are all ignoring our nation’s schoolchildren and what they are telling us about why they are turning away from nutrient-dense milk at a time when the nutrients milk delivers – that we may think they are receiving — have never been more important.
When the Pennsylvania school trial ended after one school year, a 95% reduction in the average daily volume of discarded milk was recorded. The school Student Council did an environmental project to measure this by measuring the volume of milk thrown away in unopened and partly consumed half-pint containers.
Shouldn’t we be listening to what the young people are telling us? They are our future, after all.
In the meantime, consider this: Fresh fluid milk is the most notably locally-produced dairy product maintaining dairy farm relevance in regions and communities across America. What will the dairy industry look like five years from now, even one year from now? Maybe we should be asking the schoolchildren to answer that question.
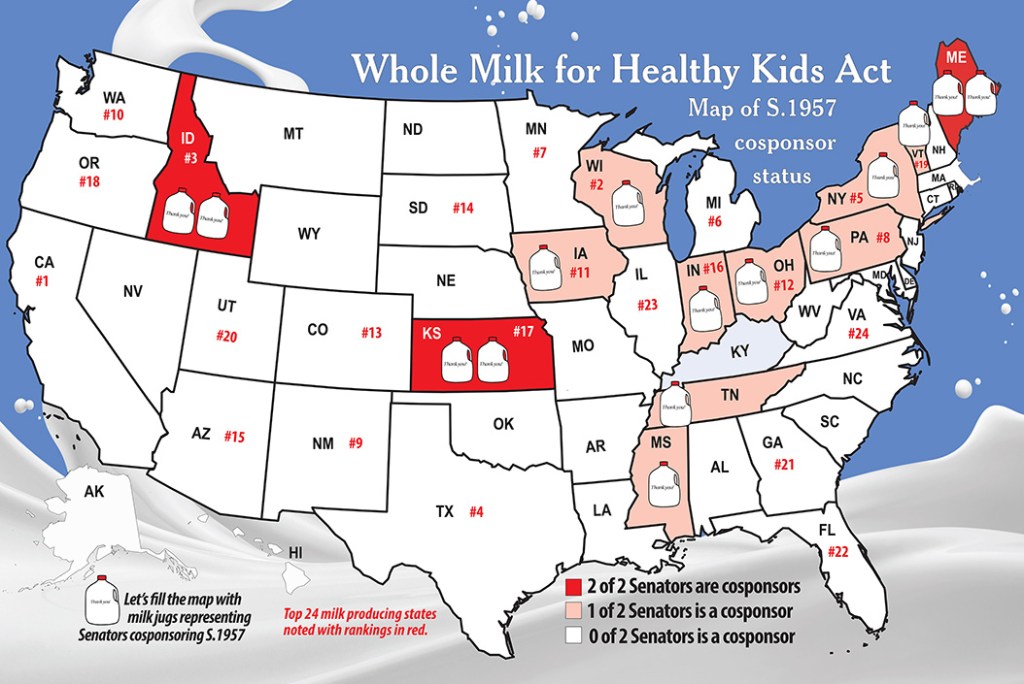
As of Feb. 14, 2024, the Whole Milk for Healthy Kids Act, S. 1957, has 15 sponsors from 12 states as illustrated on this map. Graphic by Sherry Bunting

Pingback: Seeds of doubt being sown, Part II: ‘What will processors do with all that skim?’ Oh my! | Ag Moos
Pingback: Seeds of doubt being sown, Part III: Will it reduce butterfat supply and impact industry’s cheese-focused future? | Ag Moos