Consensus evident on some key proposals, such as returning the Class I mover formula to the ‘higher of’; but 10 packages contain over 30 variations and a few new biggies.
New to the party are:
- AFBF wants to end ‘advance’ pricing of Class I;
- NAJ wants uniform component-based pricing of Class I in all Orders;
- MIG, made up of 7 fluid processors want organic exemptions, an assortment of new credits, and they want to knock $1.60 off the Class I differentials, forgetting they already get over $3.00 in ‘make allowance’ credits while not incurring those costs
- California Dairy Campaign seeks an extension to consider alternative pricing formulas
- Some proposals want to drop products (500-lb barrel cheese) from the FMMO formulas and price surveys, others want to add products (ie. 640-lb block cheese, mozzarella, unsalted butter)
By Sherry Bunting, Farmshine, June 23, 2023
WASHINGTON – In preparation for a potential national Federal Milk Marketing Order (FMMO) hearing, the Dairy Division of USDA’s Agricultural Marketing Service had a pre-hearing information session Friday, June 16. During the day-long session, held virtually through zoom, Deputy Administrator Dana Coale, Director Erin Taylor and others heard presentations of the more than 30 pieces contained in proposals submitted by 10 organizations, and they engaged in questions for clarification as well as accepting requests for data before the 10 proposals were to be modified for final submission June 20.
While the Secretary of Agriculture has not yet declared a hearing, the AMS Dairy Division has publicized the timelines and action plan.
Coale stated that mandated time frames by Congress, govern the amount of time from the point at which a proposal is received to the end of a hearing 120 days later. “All of our proposed time frames are based on keeping us focused to meet the 120-day mandate,” she said.
“Once submitted, USDA will further evaluate them, and the Secretary will make the determination,” said Coale. “If the Secretary intiates rulemaking, you will see a hearing notice containing all proposals to be heard. This will be mid- to late-July, and we would expect to move forward – if a hearing is initiated – on Aug 23 as the start of that hearing.”
The location will be Carmel, Indiana, and because of the new time constraints, new procedures will be put in place, she said.
“Expect to see a very different process than customarily done to create a very efficient process while maintaining transparency and a robust evidentiary record,” she explained, noting this includes a process for submitting testimony in advance, and a naming vs. numbering convention for exhibits.
After the hearing is noticed, there will be another information session, said Coale.
“It takes an entire village,” she stressed. “Ex parte communication does not begin until a hearing is noticed, so if you have questions or need explanation or discussion on data for submitted proposals, contact us at fmmohearing@usda.gov”
The marquis proposal is the comprehensive package submitted by National Milk Producers Federation (NMPF) that set into motion the Secretary’s call for other proposals. The NMPF package has five proposals, previously reported in Farmshine through various articles since the October stakeholders meeting hosted by American Farm Bureau in Kansas City in October 2022.
Retired cooperative executive Calvin Covington is the lead on one of the five NMPF proposals, which seeks to update skim components to more accurately reflect the percentage of protein, nonfat solids and other solids in a hundredweight of milk today.
Covington said he also expects to testify on the NMPF proposal to raise Class I differentials with a new pricing surface map, something that has not been done since 2007-08, and the proposal to return the Class I base price ‘mover’ to the ‘higher of’. The current average plus 74 cents method has been in place since May of 2019, which produced unintended consequences and losses for dairy farmers.
In a phone interview Tuesday, June 20, Covington explained that after more than a year of task force meetings and discussions via NMPF with its members and their farmer members, “We’ve gotten this far, and we have got a consensus,” he said of the NMPF package.
In addition to updating skim components and Class I differentials and changing the Class I ‘mover’ back to the ‘higher of,’ the NMPF package includes a proposal to modestly update make allowances and to discontinue the barrel cheese price in the Class III protein formula while allowing 45-day forward-priced nonfat dry milk and dry whey to be included in the formula price survey instead of the current 30-day forward-price limit.
“It took a year, and that’s pretty good, to have coast-to-coast consensus on five major proposals,” said Covington. “Then you also read the Farm Bureau’s proposal and there’s pretty good consensus there too.”
Central to both the NMPF package and AFBF package of proposals is strong support for returning the Class I mover formula back to the previous ‘higher of’ method.
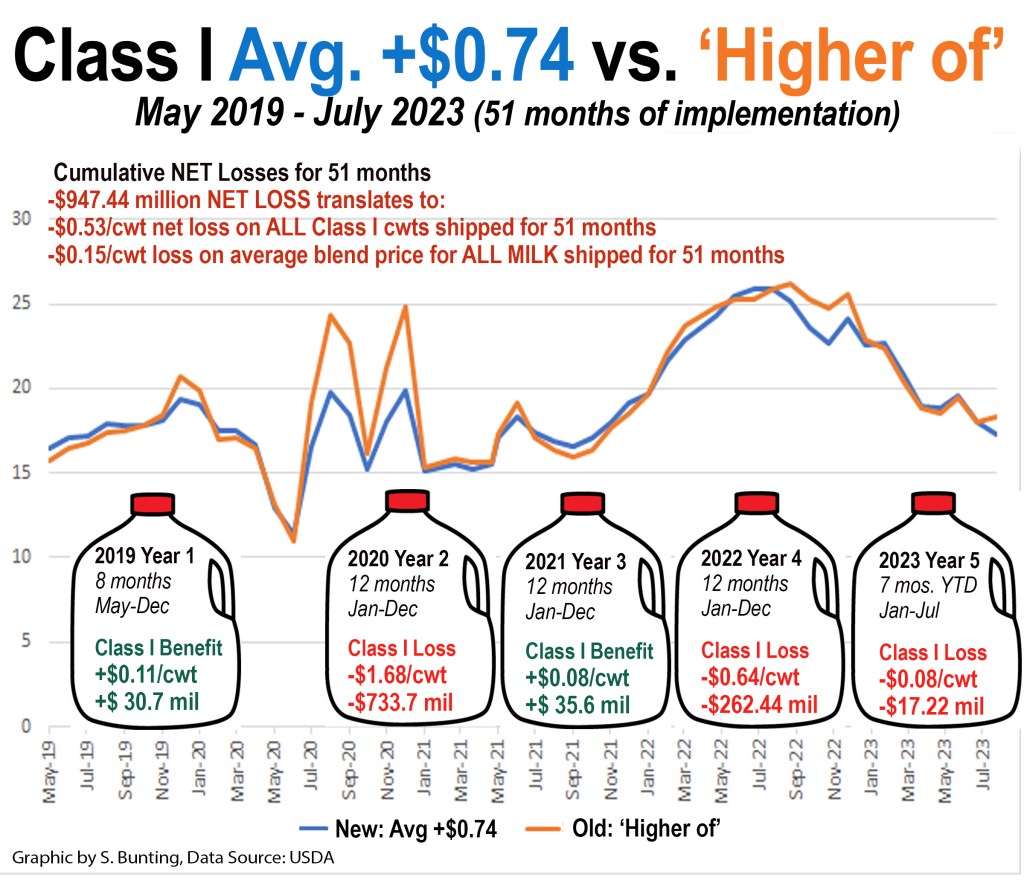
(Farmers have had a cumulative net loss of nearly $950 million, equivalent to losing 53 cents on every hundredweight of milk shipped for Class I use for the past 51 months or 15 cents per hundredweight on the FMMO blend price for all milk across all 51 months — since the change to ‘average of’ was made in May 2019 via the 2018 Farm Bill. In fact, the July 2023 Class I mover was announced June 22, 2023 at $17.32, which is a whopping $1.02 below the $18.34 it would have been under the ‘higher of’ method.)
AFBF supports NMPF’s proposal to restore the Class I mover to the ‘higher of’ Class III or IV, to drop the barrel cheese price from the Class III component and price calculation, to update component values into Class III and IV formulas, and to update Class I differentials, but notes this should be done through careful review where changes are based on a transparent record.
AFBF chief economist Roger Cryan stated that AFBF will defer to NMPF for substantiation on the Class I mover change, but if by any chance NMPF would back away from this proposal, Farm Bureau wants it kept on the table and will defend it.
On adjustment to Class III and IV product make allowances, AFBF supports this under the same logic as the NMPF proposal, but states that “such adjustment cannot be fairly undertaken except in using the data from a mandatory and audited USDA survey of, at least, those plants participating in the National Dairy Product Sales Report (NDPSR) survey.”
The difference is NMPF says it will seek mandatory surveys through legislation, whereas AFBF sees USDA as already having the authority to do this.
AFBF’s package includes some “new” proposals as well. One would add 640-pound block cheese to the Class III component and price formula and the NDPSR survey and another would add unsalted butter to the butterfat and protein calculation and the NDPSR survey.
AFBF includes a proposal to update the Class II differential to $1.56 to account for current drying costs and to adjust formula product yields and include an adjustment to the ‘make allowances’ for cooperatives and plants that “balance the market.”
The AFBF package also cites “universal milk check transparency requirements” regarding clarity to be shared on producer milk checks regarding pooled volume, Order value and actual payment for pooled and nonpooled milk.
AFBF seeks a seasonal Class I differential adjustment to “address seasonal differences in supply and demand.”
The most notably divergent AFBF proposal is one that seeks to eliminate the advanced pricing of Class I milk and components and the advanced pricing of Class II skim milk and components. It would base both on the 4-week “announced” Class III and IV components and prices instead of the 2-week “advanced” pricing factors. The advanced factors are calculated for a given month during the first two weeks of the previous month and have been part of FMMO pricing for decades.
Edge Dairy Farmer Cooperative, representing farmers in nine Midwest states shipping to 34 processors also proposes ending advanced pricing of Class I.
A newsflash proposal came from the Milk Innovation Group, which was formed within the last few years and testified at the recent Southeast FMMO hearings.
MIG is made up of seven companies — Anderson Erickson Dairy, Aurora Organic Dairy, Danone North America, Fairlife, HP Hood, Organic Valley/ CROPP Cooperative, and Shamrock Foods.
They want to REDUCE Class I differentials, whereas NMPF and AFBF support updates that increase them.
MIG companies want to establish Class I differentials that remove the “Grade A compensation” portion that has been built into all Class I differentials from the beginning, as well as removing the “market balancing compensation.”
Together, these removals would account for the $1.60 per hundredweight base differential that all FMMOs receive. As explained in the pre-hearing session, this would have the net effect of reducing Class I differentials (and producer pay prices) by $1.60 per hundredweight across all FMMOs.
In their justification, MIG writes that it is “far past time for the base Class I differential to be reconsidered in light of market changes, including the exploding growth of dairy beverage alternatives… and the exponential growth of non-fluid milk products often sold in the export market.”
(In this reporter’s analysis and opinion, reducing Class I differentials instead of raising them, ignores the fact that every Class I fluid milk processor – including the aseptic, ultrapasteurized, organic, ultrafiltered and other ‘specialty’ fluid milks – are already getting more than $3.00 per hundredweight embedded as a processor credit in the Class I base price mover by virtue of the cumulative sum of all product make allowances on the Class III and/or IV pricing factors used to establish that mover, but since they don’t make Class III and IV product, they don’t incur these costs. Now they want $1.60 more, plus “assembly” and other credits?)
The MIG also proposes exempting processors of Class I organic milk from paying into FMMO pools as long as they show they pay their producers at least the minimum FMMO price. There are a few other guard rails to this.
They also want to receive “assembly credits,” specialty credits, and a higher shrink credit (forgetting that they already get make allowance credits that don’t even apply to them).
Citing the “unequivocal decline in Class I sales,” the MIG sets the stage with its package of proposals to transition further away from pricing mechanisms that support local fresh milk in favor of aseptic, extended shelf-life milks and specialty products. Some of the companies in the MIG are making dairy beverages that are not even Class I, and several are getting big into plant-based and other non-milk alternatives and blends. (Is that a conflict of interest?)
USDA AMS also accepted further information on the prior petition by the International Dairy Foods Association (IDFA) and Wisconsin Cheese Makers Association (WCMA) to update make allowances. With this additional information, their petitions are back on the table and are based on voluntary cost surveys.
Additionally, IDFA submitted a proposed alternative method for establishing the Class I mover they call the “Floored Class I Mover proposal.” This is IDFA’s response to NMPF’s proposal to return Class I to the ‘higher of.’
The IDFA alternative is described as using the current simple average of the Class III and IV advance pricing factors to set the base Class I price, and floor the adjuster at the current 74 cents — while allowing that adjuster to increase if a two-year look-back shows it was deficient vs. the higher of. This is a complex two-years back “making producers whole” in the two-years forward with the adjuster always being floored to go no lower than 74 cents even if it turns out that this method benefited farmers vs. the ‘higher of.’
The IDFA Class I proposal contains several pages of justification for the averaging method built around “preserving price hedging and risk management” for processors, particularly those in the ‘value-added’ category,” such as ultrafiltered and aseptic Class I milk products.
But it doesn’t end there…
National All Jersey (NAJ) brought forward its proposal, explained by Erick Metzger. “One mirrors NMPF’s proposal to update skim component factors in the Class III and IV formulas, except we want to see it be a simple annual update based on the previous year’s average, with an appropriate lag time to address risk management tools instead of being based on a three-year average,” he said.
In addition, NAJ proposes that FMMOs 5, 6, 7 and 131 (the Southeastern Orders and Arizona) become multiple component pricing (MCP) Orders instead of pricing on a fat/skim basis.
NAJ also proposes Class I payment requirements to be based on MCP pricing instead of skim / butterfat in all FMMOs, nationally.
“We are proposing uniform pricing across all orders — both on how processors pay for components and how producers are paid for components,” said Metzger. “Extensive updates are needed to Orders 5, 6, 7 and 131, and the needed Order language already exists in the other Orders.”
The NAJ proposal notes that Class I should be paid on actual solids, instead of valuing the skim on a skim basis. “In our proposal, it would be valued or priced on actual skim components,” he said.
What this means is if a dairy farm’s actual components processed (in Class I) were below the standard components in the Class III or IV formulas, the processor obligation would be less; and if the farm’s skim components are greater than the standard, then the obligation of Class I processors to the pool would be more. In short, accounting for actual skim components in the NAJ proposal, would replace the current pricing of Class I skim on a pounds of skim basis.
Select Milk Producers cooperative submitted proposals to update product yields to reflect “actual farm-to-plant shrink,” to update the butterfat recovery factor and to update nonfat solids yields. According to their own limited 5-year-average analysis the three proposals combined would net 13 cents/cwt on the Class III price and 42 cents/cwt on the Class IV price, but they’ve requested more data from USDA AMS to analyze — if their proposals are accepted for a hearing.
For its part, Edge Cooperative states in a cover letter to its proposals that a hearing should occur after the farm bill. “There is no imminent crisis that would present a compelling reason to initiate a hearing before the next farm bill is enacted,” the proposal states.
In the farm bill, Edge seeks a mandatory cost of processing survey before make allowance updates could be heard. Edge also seeks legislative language to expand flexibility to base individual FMMOs around something other than uniform pricing, to be determined on an Order by Order basis. This “flexibility” was explained by Lucas Sjostrom and Marin Bozic at the Farm Bureau stakeholders meeting in Kansas City last October.
However, Farm Bureau’s package of proposals asserts that there is no reason to hold off on a hearing while waiting for a farm bill, and indeed seeks the fastest resolution to the Class I ‘mover’ issue. Furthermore, Congress previously mandated timelines that don’t allow “waiting” once proposals are received by USDA. This process is in motion, unless Secretary Vilsack refuses a hearing on any of the proposals.
AFBF, in fact, cited areas of the Agricultural Agreement Act that give USDA authority to do mandatory cost surveys, without further legislation, because the Secretary has discretion to require any reporting deemed necessary from FMMO participating plants.
On the Class I ‘mover, Edge proposes two options, either a Class III-plus option if the ‘advanced pricing’ is retained or if the ‘higher of’ option is used, then to base it on final 4-week announced skim milk prices each month. This option would effectively end the 2-week advanced pricing factors and advance pricing of the Class I ‘mover,’ which has also been proposed by AFBF.
The Edge proposals include a request to align make allowance changes so that they don’t impact ‘risk management tools’ and a proposal to add Order formulation language about the information handlers shall furnish to producers with the intent of “transparency in producer milk checks.”
The California Dairy Campaign’s proposal asks USDA to extend the proposal deadline and to add mozzarella to the Class III component and price formula and the NDPSR survey. They also want consideration of “alternative pricing formulas that guarantee dairy farmers are paid according to current market rates.”
The California proposal includes a National Farmers Union (NFU) Dairy Policy Reform Special Order of Business that was passed at the 2023 NFU Convention in San Francisco. It states opposition to the call for a federal milk marketing order hearing, noting that, “If a hearing is granted, it is essential that any modifications to the federal order minimum pricing formulas take into account the volume and value of all dairy products, particularly high-moisture cheeses such as mozzarella.”
Dairy Pricing Association (DPA) submitted a few proposals explained by Wisconsin dairy farmer Tom Olson. One seeks to pay Grade B milk at FMMO minimums, but without a producer price differential (PPD).
DPA also proposes a supply-balancing feature, whereby milk handlers notify farms at least 7 days prior to milk disposal action, stating the baseline production needs, how much to reduce production, and for how long, with farmers making this reduction by dumping (or not producing) this milk.
In effect, the DPA proposal includes a processor-led supply management program, not a government intervention. But to do it, the FMMOs would be the arbiter, and therefore all Orders would have to be amended to require 100% mandatory participation and pooling of all U.S. milk. Something like that may require legislation since a producer referendum bloc-voted by cooperatives could vote it down, and it’s unclear how unregulated areas would be included since states like Idaho already voted the FMMOs out.
Currently, only Class I milk handlers are required to participate in FMMOs within marketing areas that have FMMOs. Participation is voluntary for most Class II, III and IV processors. Over the past three years, roughly 60% of total U.S. milk production has been pooled on FMMOs.
-30-