By Sherry Bunting, Farmshine, Jan. 31, 2025
SAVANNAH, Ga. and EAST EARL, Pa. — As part of his annual outlook for Southeast milk markets, and also in his look ahead for the milk market nationally and in the Northeast, well-respected retired milk co-op executive Calvin Covington broke down the final USDA Federal Milk Marketing Order (FMMO) formula changes into three categories: The positive, the negative, and the unknown. (Plus, there is also the ‘unvetted.’)
Covington spoke to over 300 attendees from 10 states at the 2025 Georgia Dairy Conference in Savannah on Jan. 20th, just a few days after USDA’s announcement that producers in each of the 11 FMMOs approved the final rule. Then, on January 28th, he was in eastern Lancaster County, Pennsylvania speaking to 250 dairy farmers on this topic at R&J Dairy Consulting’s 18th Annual Dairy Seminar at Shady Maple Smorgasbord.
The FMMO changes will be implemented June 1, 2025, except for the increased milk composition factors, which will be delayed six months due to impacts on “risk management.”
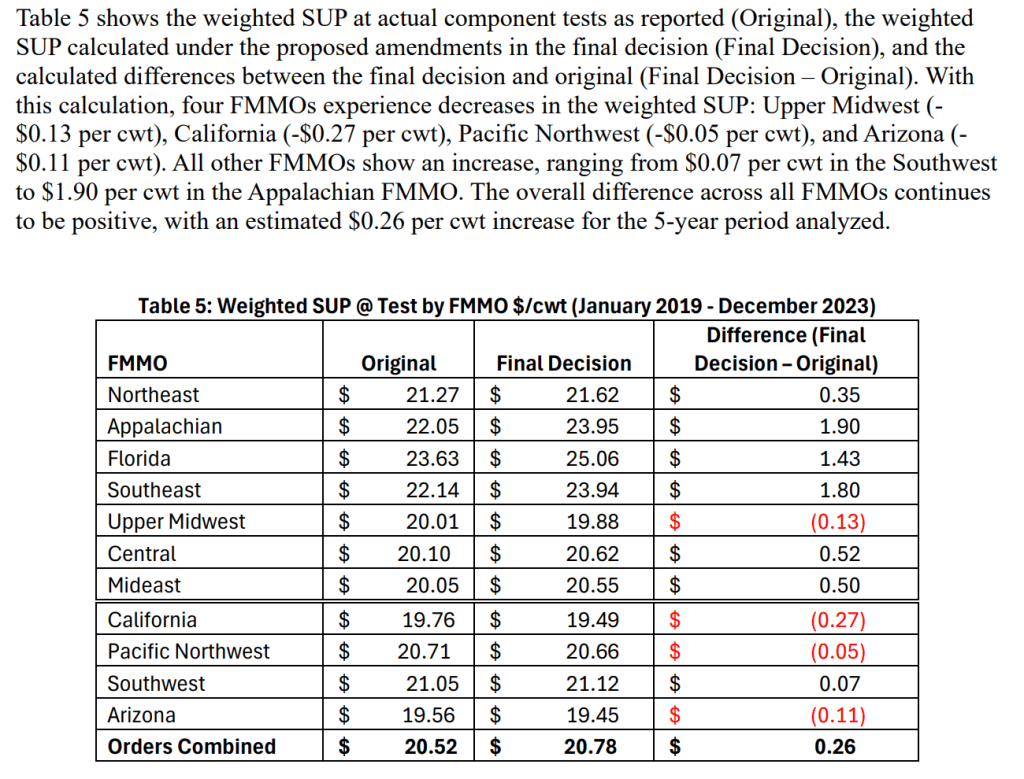
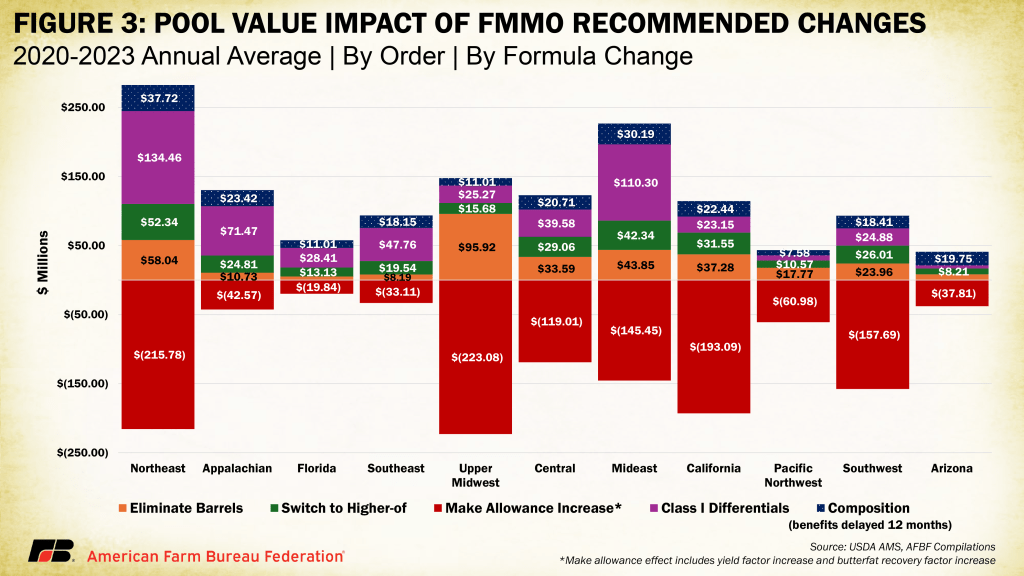
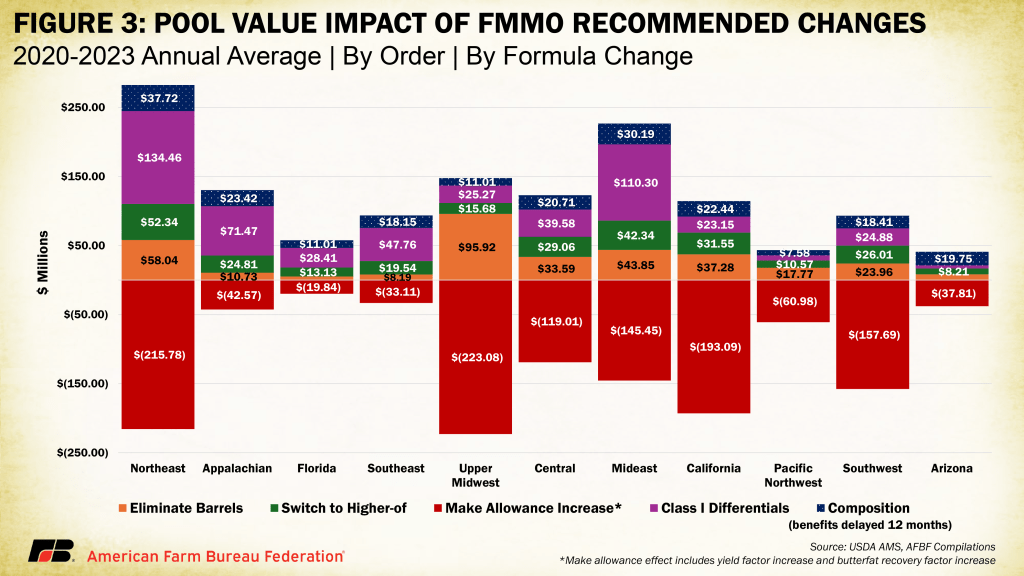
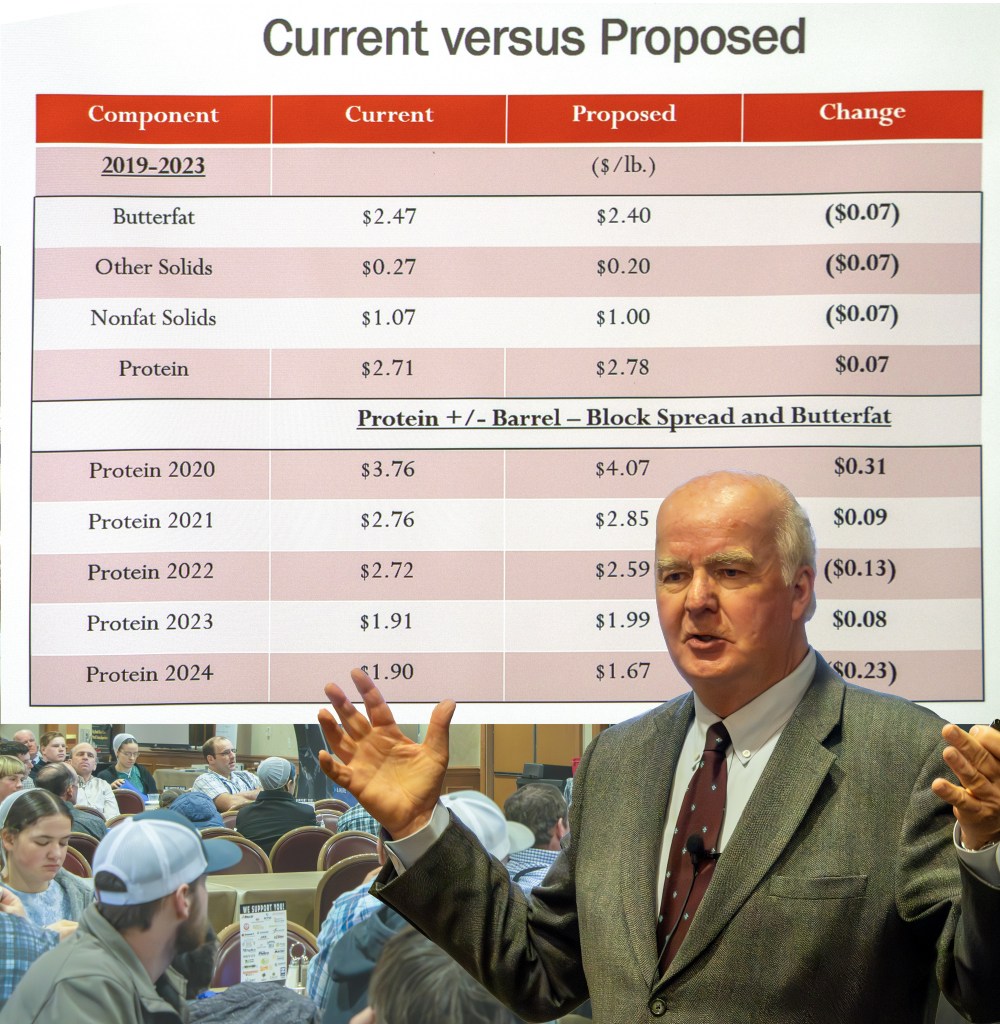
Covington shared collective analysis based on USDA’s backward-looking data (2019-23), showing that all six pricing changes, combined, would have benefited producers by 26 cents per hundredweight across all FMMOs, nationwide, during those years.
“But, like the disclaimer on a financial prospectus, ‘past performance is not an indicator of future results.’ It is all relative,” he said. “The three Orders of the Southeast are by far the biggest beneficiaries, but going forward, there are a lot of things we just don’t know.”
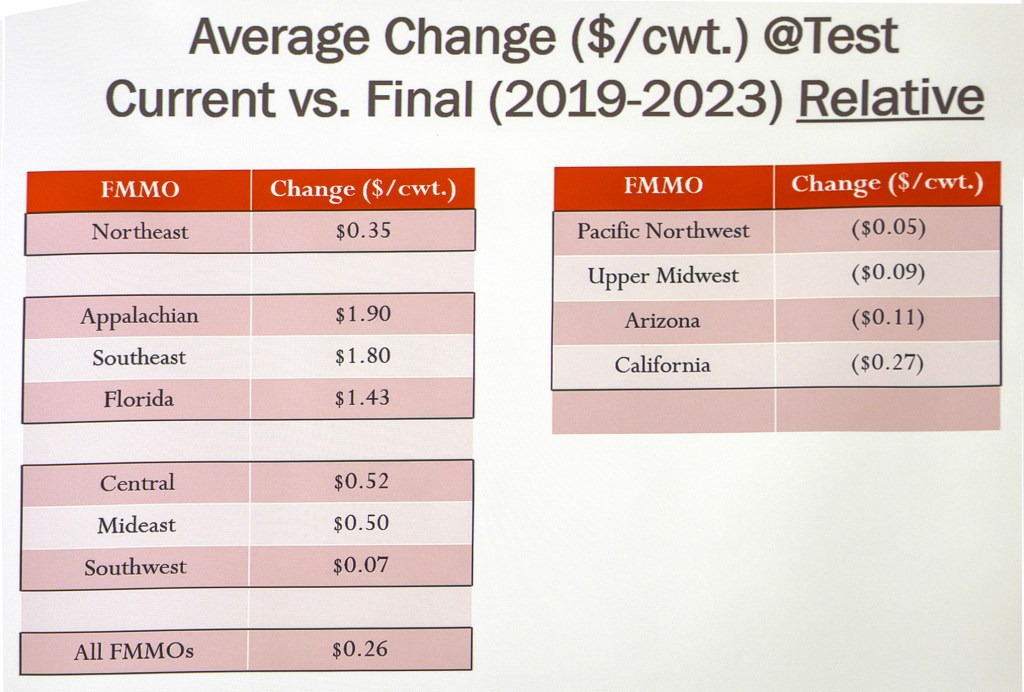
Orders with estimated negative net impact at test are: Pacific Northwest (124) -5 cents; Upper Midwest (30) -9 cents; Arizona (131) -11 cents; and California (51) -27 cents.
Orders with estimated positive impacts at test are: Appalachian (5) +$1.90; Southeast (7) +$1.80; Florida (6) +$1.43; Central (32) +52 cents; Mideast (33) +50 cents; Northeast (1) +35 cents; and Southwest (126) +7 cents.
The good
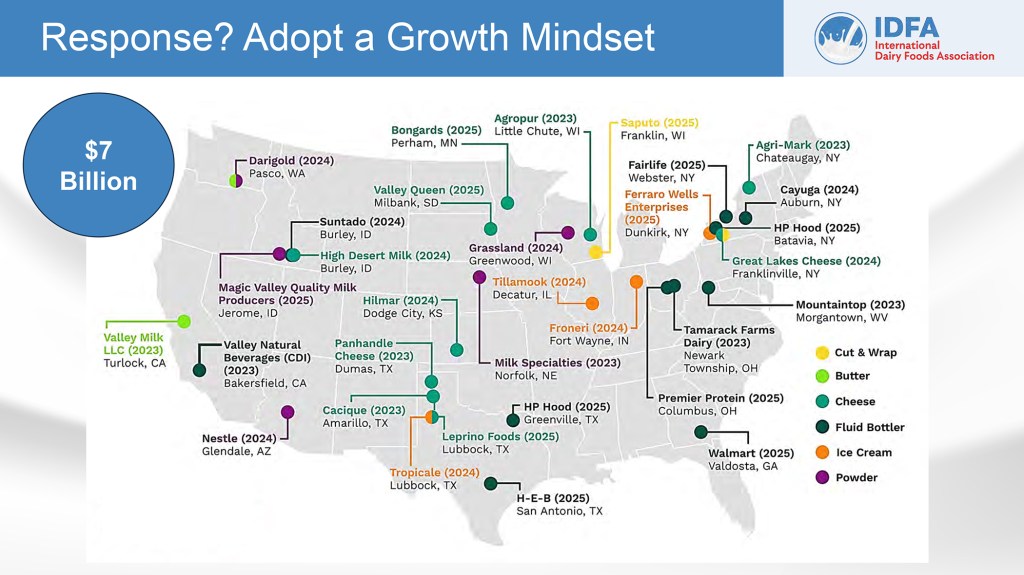
“The Southeast will see the majority of benefit, with the updated Class I differentials,” Covington reported, illustrating how they vary by location for an average increase of $1.42 per cwt across the country – but only for Class I milk. The three Orders of the Southeast will see more of this benefit because they have the largest Class I differential increases and their blend prices are predominantly Class I.
A University of Wisconsin-Madison study had previously looked at where the plants are and where the milk is, in order to think about moving milk from where it more is produced to where it is needed.
The highest differential increase is along the route 85 corridor, beginning near Atlanta, up into West Virginia, where there are plants but no milk. Interestingly, his chart showed that the smallest increases for the region are in Florida locations as well as Valdosta, Georgia, where the new Walmart milk plant is being built.
In the Northeast, Covington said dairy farmers will have to get used to what this looks like on their milk check, and they will also see more incentive to move milk South under these new differentials.
“Each county has a differential assigned to it,” he said, pointing to the area of the R&J Meeting, near New Holland seeing a $1.40 per cwt. increase in Class I differential, but this is a smaller increase compared to the much larger increase put on at Boston, Mass.
“That big increase in Boston is because there’s not any milk around there, and it’s raised to get the milk to move to the people there,” he said. This means that even though the new Class I differential will raise the Class I price in New Holland, “farmers will have to get used to seeing their location differential as a bigger negative on the milk check,” because the increased differential in Boston is so much bigger.
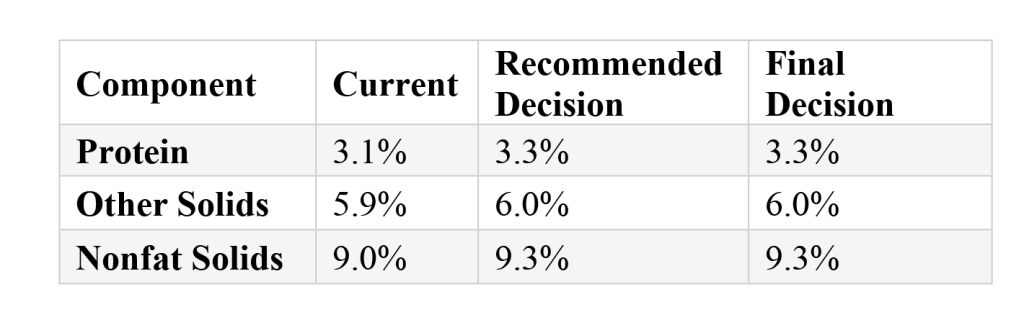
The milk composition factor updates are straightforward, he said, yielding about a 35 cents per cwt benefit to the Class I milk price in all FMMOs, and will raise the standardized skim value of the other classes in the three southeastern Orders that are still priced as fat/skim instead of by multiple component pricing.
The bad
The make allowance increases will lower the price for butterfat and other solids value, he said, “but we don’t know what will happen with the protein price because of the elimination of the barrel cheese prices from the formula.”
This will manifest as lower butterfat and other solids component prices for the Northeast, he said. “We would expect the protein price to be higher, based on history, but that depends upon the block to barrel price spread and its relationship to the butterfat price.
The unknown
Historically, the 500-pound barrel cheese price was lower than 40-pound block price.
“Last year, however, barrels have been higher, so we don’t know,” said Covington.
Also in the unknown category is the return to the ‘higher-of’ as USDA’s method for setting the base Class I skim price.
“In the past five years, the average-of method cost dairy farmers millions of dollars, but we don’t know going forward if the skim factors (Class III vs. Class IV) will get back to being closer together, which would lower prices. If the spread stays wide, this change to the higher-of will increase prices,” he explained.
When asked if the Covid pandemic created the loss in Class I value under the average-of vs. higher-of, Covington said the Covid period — while most obvious — only accounts for one year out of five years in which the spreads between Class III and Class IV and between block and barrel cheese were detrimental.
“The thing going forward is, we just don’t know,” he said.
The unvetted
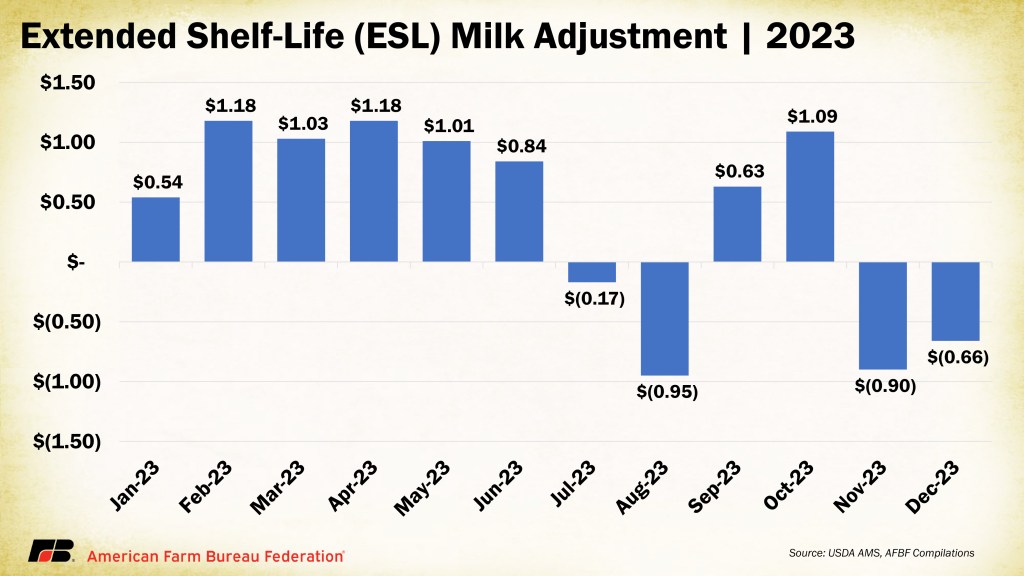
The sixth change is not listed separately in the Jan, 16th USDA notice to trade, and it was not part of any hearing proposal. Covington said he views the extended shelf life (ESL) adjuster as “a new class of milk.”
“The ESL adjuster is only on Class I. You’ll have a Class I mover skim price that will be calculated for conventional milk based on the higher-of III or IV,” he said. “Then you need a big spreadsheet to show what’s going to happen next. They’ll look 36 months previous to 12 months previous at the difference between the higher-of and the average-of, and that will be the adjuster to use for ESL milk that month.”
He estimates the ESL adjuster would have averaged -30 cents in 2024, but for some months it would have been a plus.
“My initial analysis is that it will not make a whole lot of difference in the short term, but we just don’t know going forward if some will try to manipulate this,” he said. “My concern is that it was not proposed at the hearing at all, and there’s no definition for extended shelf life. I know being in this business all these years, if there is a way to work around it for a benefit, they will find a way to do it.”
When asked about the competitive issues between conventional and ESL fluid milk and between out-of-area packaged ESL milk competing with in-area fresh milk, Covington observed potential competitive issues between conventional and ESL milk in the same area.
“You’ll have two different costs at the same location. What has always been the beauty of the Federal Order system is having the same raw product costs at the same location,” he said, adding that new ESL plants are being built and others are expanding.
“As ESL grows… there could be some months with a price advantage,” Covington suggested, pegging that difference historically to be as much as $1.00 per cwt in some months. “That kind of difference can create disparity between conventional and ESL milk.
“The thing is, we just don’t know, going forward, what it’s going to look like.”
Covington urged farmers to pay attention and be involved. Federal Order reforms are a slow process involving a lot of time and compromise. Changes this big only happen about every 25 years, he said.
He noted that Farmshine has kept dairy farmers “well-informed” with effective reporting on the markets and the FMMO process.
He said that as more manufactured products are sold and less fluid milk, compared with 25 years ago, the future could look different if future administrations and lawmakers feel differently about the pricing of milk. If manufacturers perhaps choose not to participate, FMMOs could some day be looked to primarily for handling the payments and test weights.
However the future plays out, Covington urged: “Stay informed and be involved because it is your milk check.”
-30-