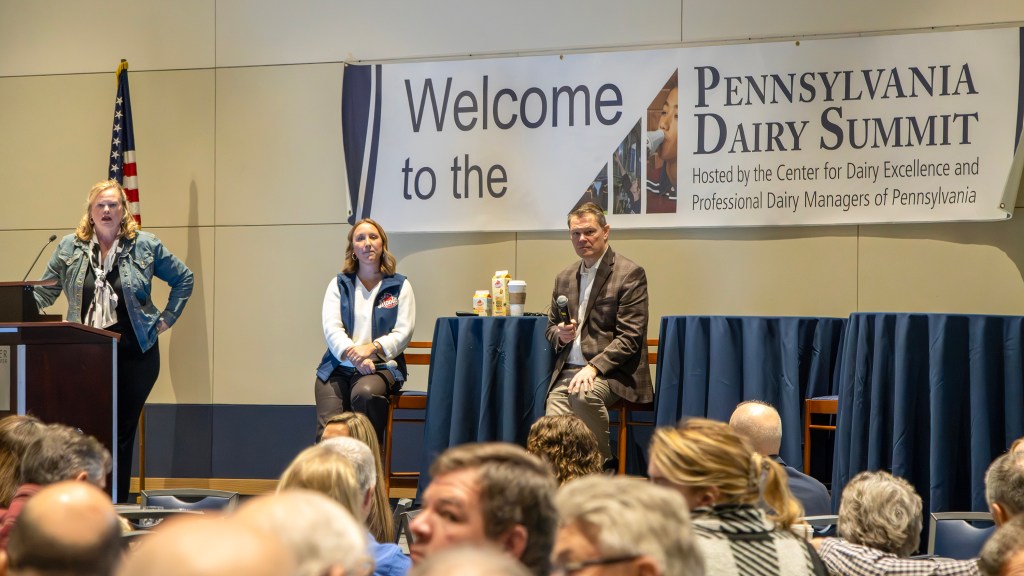
At the 2025 Pennsylvania Dairy Summit, Paul Ziemnisky, DMI’s head of wellness, innovation, and business development, and Rebecca Pfeffer, Maola brand manager, with moderator Amy Mearkle (left) spoke about fluid milk innovation in which extended shelf life (ESL), otherwise known as ultra pasteurized (UP) milk, is seen as the gateway to new products aiming to meet ‘functional needs’ of consumers.
By Sherry Bunting, Farmshine, March, 2025
STATE COLLEGE, Pa. – Food-as-medicine, food-and-medicine, fun-and-portable, young kids talking about pre-aging, on-the-go snack and beverage convenience, the quest for guilt-free ways to unwind with fewer calories than wine, the growing double-income-no-kids (DINK) consumer landscape that is focused on wellness, consumer shifts from coffees to teas, the surge in protein demand, and the growth in sales of lactose-free milk…
These are some emerging trends mentioned during a panel about extended shelf life (ESL) milk as the gateway to dairy checkoff’s Milk Molecules Initiative during the Pennsylvania Dairy Summit last month.
In the Feb. 21st Farmshine, we brought you part one, a panel overview in this three-part series. In this second installment, we dig into what Dairy Management Inc (DMI) is doing with protein in the fluid milk space, and the technologies they are working on to separate molecules.
This public launch of the Milk Molecules Initiative (MMI) comes after 10 to 15 years of work through the pre-competitive industry collaboration vehicle – The Innovation Center for U.S. Dairy, a 501c6 established by DMI in 2008.
What we’ve learned is that MMI — as a fluid milk strategy — began even before the formation of DMI’s Fluid Milk Innovation Task Force seven years ago. It goes all the way back to 2010, right about the time whole milk choice was abolished in schools.
This strategy has been developed to discover, strip out, and repurpose the “functional benefits” of specific bioactive compounds, or molecules, in milk. The concept goes back to the early alliance between Fonterra and DMI, with headquarters less than three miles apart in the suburbs of Chicago around O’Hare Airport.
This strategy has been under development via research grants from USDA, NIH, and the National Dairy Council to the Dairy Research Institutes at four university locations, including the Barile Lab at the University of California-Davis. There, researchers have worked on isolating compounds from both human and bovine milk, and more recently, student researchers have been working on a DMI project “building a digital ecosystem and platform for these milk compounds.”
The Feb. 2022 memorandum of understanding between DMI and Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, is tying-in the human health linkages to specific bioactive compounds in milk, and the Feb. 2024 DMI partnership with PIPA, an artificial intelligence (AI) platform, is accelerating the knowledge gain in how to break down milk’s so-called “bioactive family tree” to leverage functional milk products with new health benefits.
“We are finding the molecules in the whole milk matrix and picking things that are on the ‘whey stream’ as one area of focus, such as stripping out the lactorferrin,’” said Dairy Summit panelist Paul Ziemnisky, head of wellness, innovation and business development for Dairy Management Inc. (DMI), who has spearheaded the work of the Fluid Milk Innovation Task Force.
“We have partners talking about building a lactoferrin plant centered on just one of thousands of molecules in milk. We are looking at how to protect this molecule so it doesn’t lose its bioavailability, so we can put it back into dairy (post-processing),” he said.
Ziemnisky observed how past checkoff messaging has touted things like: “chocolate milk as a recovery beverage.”
Today, he said, “We’re going beyond that. We’re looking at ways to add milk to milk and to use these concepts to give it a different look and to capture huge value potential.”
How does DMI plan to partner with industry to capture this value? By linking milk and technology to create new products.
According to Ziemnisky, the MMI is looking aggressively at encapsulation and separation technologies as well as drying technologies that can be patented while testing the concepts with consumers to “learn how to talk about it.”
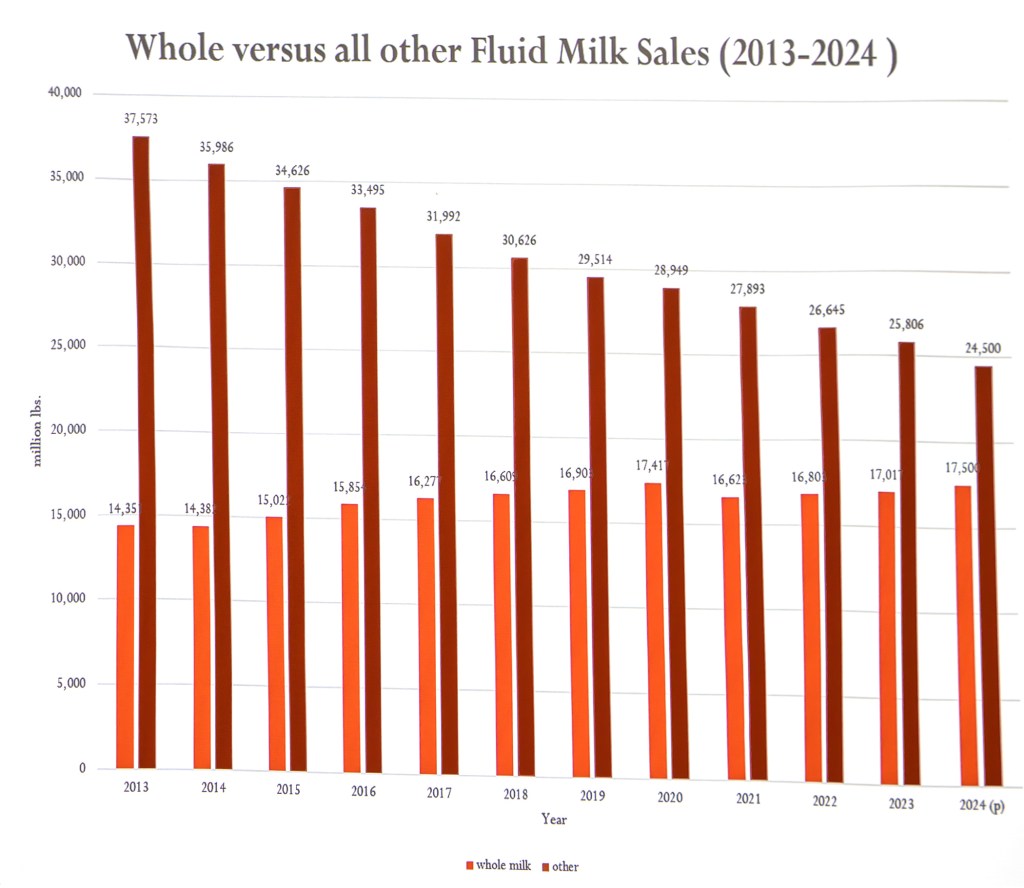
“If we focus on whole milk, we miss these market optimizers,” Ziemnisky declared. “Whole milk is for the 17% of traditionalists. We must innovate this category. We’re giving consumers a reason to understand what they need.”
He says MMI and ESL are pathways to get “milk” into more top-demand moments to capture a larger share of the $159 billion total beverage category.
(More ultra processed beverages are just what global consumer packaged goods companies are famous for. But is this what consumers really want? And will the ‘huge value potential’ trickle down to farm milk checks?)
According to Ziemnisky, there is at least $2 billion in new investment coming into the beverage space across geographies. “But it’s not your father’s Oldsmobile. Those new plants are filtration and separation, and we can add functionality to it.
“There are things we know of that we can’t even talk about yet,” he said as he gave a snapshot of where MMI is, and what is yet to come.
He cited a proliferation of ESL milk beverages that are mainly lactose-free, high protein milks as the gateway to molecular separation. Examples included the ESL capabilities at the Maola plant in Philadelphia, the national launch of Milk50 by DFA, the new nutrition line of beverages developed by Dairy Gold, Nestle’s new line made exclusively for Target, and others.
Asked if these new products are taking sales away from non-milk alternatives or traditionally branded milk, Ziemnisky said DMI’s work with MilkPEP shows that the plant-based beverages – on a volume and value basis – are “over-shelved.”
“They haven’t grown their category, their volume is declining. Those guys are eating themselves — going after each other. They’re not going after us anymore because they can’t. We win with nutrition and value. When we see all the innovation that is coming into dairy, we’re taking our space back by meeting the functional needs of the consumer. The quality of the protein is in demand now,” he said, confirming data showing that, “People are coming back to us because of the nutrition and the quality of the protein.”
During questions, he dug into the health and wellness “playbook” that checkoff has created with the help and blessing of USDA and has put into the hands of the top people at all of the big companies in food processing and retailing.
“We’ve traditionally undersold our nutritional benefits, and that’s changing,” he said.
Where MMI comes into the picture is to identify the bioactive molecules for separation and marketing linked to specific health claims that can go on a label.
A graduate student in the audience said the presentation gave her “a lot of hope in the future as a scientist.” She asked if DMI has noticed any difference in regional trends related to consumers, and specifically wondered what is happening in California?
Ziemnisky said California was moving the other direction. “They like to try things out there,” he said, explaining that the dairy industry is so volume- and scale-focused that pilot products are not the norm.
“California is coming back. California has assets that do smaller runs to try things. Last year, California grew (beverage milk sales) at a faster pace, whereas the Northeast market is so heavily regulated,” he said, adding that government regulation puts pressure on local retailers who want to try things.
DMI’s role is to test and learn, he explained: “We help processors prove these markets to retailers. Value-add is 30% of the dollars in the fluid milk category today. We went to 30% from just 10% just 10 years ago. We are targeting both volume and value with our retail and direct sales teams.”
One attendee asked what checkoff can do about the out-of-stock issues at retail, noting that perhaps fluid milk sales would increase if the dairy cases were consistently well-stocked.
“When we ask the store people, they say we don’t do the orders, it all comes from above us,” the questioner said.
Ziemnisky replied: “They are not telling you the truth. The real out of stock rate nationally is 3%. The problem is they are not managing their inventory. The inventory is there, but not the labor.”
“What we run into is the problem is store help,” said John Chrisman of ADANE, jumping into the conversation, noting new laser-system camera technologies are coming within the next five years to issue alerts about what is “flying off the shelves.”
In the meantime, he told attendees to report out-of-stocks to ADANE so they can get it resolved.
Another question asked was how farmers can feed or manage their herds to hit higher levels of functional bioactives like lactoferrin.
Ziemnisky said that’s a question for the milk buyers’ field service personnel, but in general, feeding cattle to hit higher component levels will raise the functional level of milk molecules like lactoferrin.
This reporter asked Ziemnisky what DMI is doing to know if there is any change in the protein structure with the further processed options: “How are we protecting that message on whey protein by protecting its structure through the ultra pasteurization process?”
(The only published research we could find was an NIH study showing heat and mechanical processes of ESL packaging change the structure of the protein, namely the whey protein.)
Ziemnisky replied that DMI is “doing significant work” on the nutrition research side to prove the efficacy of dairy’s high quality protein vs. other proteins.
“And on the product science side, we’re investing significantly in everything from the clarity of protein, so you can put it into other products, to the quality as it goes through different processes that it stays stabilized. We work with the industry on what are the needs we can solve,” he assured.
On follow up questioning about protecting the protein, he added that, “Encapsulation is just one technology we’re doing to preserve the bioactive pull, and we have other things underway as well. We also look at the byproducts. What do we do with lactose coming through on the lactose-free? What do we do with the permeates on the cheese, the passive whey? These are where we’re doing work to create products from the bioplastics all the way to the functional ingredients.”
Bottom line, he said: “Whey was the bastard child, and now it is the largest gaining market share because of demand for high quality proteins. We are seeing the fractionation piece of this, the precision nutrition, the new players coming in and doing research on different compounds, driving whey to where it is today vs. 20 years ago.”
With an estimated 6300 molecules in milk identified by artificial intelligence, all located within the 13% of milk that is the solids, Ziemnisky expressed excitement about the future.
“We are at the cusp of this, and with our artificial intelligence partnerships, we are getting the learnings in 2 to 3 years that used to take 10 years,” he suggested. “This is moving fast toward a sustainable future with zero-waste circular milk plants.”
-30-