Editorial Analysis: Tumultuous 2024 spills over into 2025 – Part One
By Sherry Bunting, Farmshine, January 3, 2025
EAST EARL, Pa. – Year 2024 was tumultuous, and 2025 is shaping up to be equally, if not more so. Spilling over from 2024 into 2025 are these three areas of potential for good news to trump bad nutrition policies that are having negative impacts on dairy farmers and consumers.
Farm bill and whole milk bill
Both the farm bill and the whole milk bill showed promise at the start of 2024. No one championed the two pieces of legislation more than House Ag Committee Chairman Glenn ‘GT’ Thompson (R-15th-Pa.). He even found a way to tie them together — on the House side.
The Whole Milk for Healthy Kids Act made it farther than it ever has in the four legislative sessions in which Thompson introduced it over the past 8 to 10 years. It reached the U.S. House floor for the first time! But even the overwhelming bipartisan House vote to approve it 330 to 99 at the end of 2023 was not enough to seal the deal in 2024.
That’s because over in the U.S. Senate, then Ag Committee Chairwoman Debbie Stabenow (D-Mich.) blocked it from consideration — despite over half her committee signing on as cosponsors.
GT Thompson, found a workaround to include it in the House farm bill, which passed his Ag Committee on a bipartisan vote in May. The language was also part of the Senate Republicans’ draft farm bill under Ranking Member John Boozman (R-Ark.)
It too fell victim to Stabenow dragging her feet in the Senate. By the time the Ag Chairwoman released a full-text version of the Senate Democrats’ farm bill, little more than 30 days remained in the 2023-24 legislative session.
Key sticking points were the House focus on dollars for the farm side of the five-year package. It put the extra USDA-approved Thrifty Food Plan funding into the overall baseline for SNAP dollars and brought Inflation Reduction Act climate-smart funds under the farm bill umbrella while removing the methane mandates to allow states and regions to prioritize other conservation goals, like the popular and oversubscribed EQIP program.
Attempts to broker a farm bill deal failed, and on Dec. 20, another one-year extension of the current 2018 farm bill was passed in the continuing resolution that keeps the government funded into the first part of 2025, without amendments for things like whole milk in schools. However, Congress did manage to provide $110 billion of disaster relief for 2022-24 hurricanes, wildfires, and other events. Of this, roughly $25 billion will go to affected farmers and ranchers, plus another $10 billion in economic disaster relief for agriculture.
Looking ahead, there is good news for the farm bill and whole milk bill in the new 2025-26 legislative session. The House Ag Committee will continue under Rep. GT Thompson’s leadership as Chairman. On the Senate side, whole milk friendly Boozman will chair the Ag Committee. With Stabenow retiring, Sen. Amy Klobuchar (D-Minn.) will serve as Ranking Member, and she previously signed on as a Whole Milk for Healthy Kids Act cosponsor in March 2024.
The whole milk bill will have to start over again in the Education and Workforce Committee with another vote on the House floor. It was enthusiastically supported by prior Education Committee Chairwoman Virginia Foxx (R-5th-N.C.). Her years of chairing this committee have expired, but the good news is Rep. Tim Walberg (R-5th-Mich.) will step in, and he was an early cosponsor of the Whole Milk for Healthy Kids Act in the 2021-22 and 2023-24 legislative sessions.
New Dietary Guidelines
The 2025-30 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee (DGAC) submitted its ‘Scientific Report’ to the outgoing USDA and HHS Secretaries on Dec. 19, 2024 — just 40 days before they head out the door to be replaced by incoming Trump appointees.
The Report is the guidance of the so-called ‘expert committee’ that reviews evidence and makes recommendations for the Secretaries of USDA and HHS to formalize into the 2025-30 Dietary Guidelines for Americans (DGAs). This process occurs every five years.
The DGAs are used in all USDA feeding programs, including school lunch, childhood daycare, and eldercare institutional feeding, as well as military mess halls. They also inform food offerings in many other controlled settings.
The bad news is the Report has gone from being increasingly pro-plants over the past nine cycles to being outright anti-animal in this 10th cycle.
The good news is that dairy keeps its special spot on the so-called ‘My Plate.’ The bad news is that despite acknowledging evidence about the benefits of milkfat in nutrient dense milk and dairy foods, the DGAC rated the evidence as ‘limited’ – largely because USDA screened much of it out of the review process.
In the section on under-consumed nutrients of public health concern, especially for children and elders, the DGAC noted that whole and 2% milk were top sources of three of the four: Vit. D, calcium and potassium. Even this was not enough to persuade them to loosen the anti-fat grip that governs milk in schools, daycares and eldercare.
The DGAC states in its Report that their ‘limited access’ to research showing positive relationships between higher fat dairy and health outcomes was “too limited to change the Guidelines.”
They even doubled-down on the beverage category by recommending against flavor-sweetened fat-free and low-fat milk and that water be pushed as the primary beverage.
In the Report, the DGAC also doubled-down on saturated fat with recommendations to “reduce butter, processed and unprocessed red meat, and dairy for replacement with a wide range of plant-based food sources, including plant-based protein foods, whole grains, vegetables, vegetable (seed) oils and spreads.”
This opens the door for more non-dairy substitutes beyond soy-milk, which is already allowed in the dairy category. In fact, the Report looks ahead to future cycles changing the name of the dairy category to broaden what qualifies as makers of new dairy alternatives improve their nutrition profiles via ultra-processing. At the same time, the DGAC punted the ball on the question they were given about “ultraprocessed” foods and beverages, stating they didn’t have access to enough evidence on health outcomes to answer that question. (The next HHS Secretary might have something to say about that.)
Other animal-based foods such as meat and eggs took a big hit this cycle. The 2025-30 Report uses stronger methods for discouraging consumption. They recommend moving peas, beans and lentils out of the vegetable category and into the protein category and listing them FIRST, followed by nuts and seeds, followed by seafood, then eggs, and lastly meat.
Once again ‘red meat’ is mentioned throughout the report as being lumped in with ‘processed meat’ even though not one stitch of research about negative health relationships with processed meats included any unprocessed red meat in the studies! Clearly, consumption of whole, healthy foods from cattle is in the crosshairs. This 10th edition of the Scientific Report just continues the trend.
As in past cycles, a whole core of research on the neutral to beneficial relationships between consumption of saturated fat in high-protein, nutrient-dense foods was screened out of the DGAC’s review process by current Ag Secretary Vilsack’s USDA.
This Report essentially sets the stage for ultra-processed plant-based and bioengineered alternative proteins to play a larger role in the institutional meal preps of American schools, daycares, eldercare, and military.
But here’s the good news! The DGAC was late in finishing its 2025-30 Scientific Report!
The law requires a 60-day public comment period before USDA and HHS formulate the actual Guidelines for 2025-30. This mandatory comment period ends Feb. 10, 2025. Comments can be made at the Federal Register link at https://www.regulations.gov/document/HHS-OASH-2024-0017-0001
By the time the comment period ends, Vilsack and company will have left town. Let’s hope Senators confirm Trump appointees before the public comment period ends on Feb. 10 so their eyes are on this before the bureaucracy finishes the job.
This is a golden opportunity for the dairy and livestock sectors, along with health and nutrition professionals and health-conscious citizens to weigh-in. (Look for ways to participate in a future Farmshine.)
Meanwhile, commenters can remind the incoming Secretaries of how flawed the DGA process has become; how Americans, especially children, have become increasingly obese with increasing rates of chronic illness and underconsumption of key fat-soluble nutrients during the decades of the DGA’s increasingly restrictive anti-fat, anti-animal dogma.
Commenters should point out the fact that the Committee was not provided with all of the evidence on saturated fat. This is a message that is likely to land well with USDA Secretary designate Brooke Rollins and HHS Secretary designate Robert F. Kennedy Jr. In fact, RFK Jr. is on record opposing the low-fat dictates and has said nutrition will be among his first priorities, if he is confirmed by the Senate for the HHS post.
FDA’s final rule on ‘healthy’ labeling
In the mad rush at the end of 2024, the FDA released its final rule about using the term “healthy” on the label of foods and beverages.
This process was outlined in the White House National Strategy on Hunger, Nutrition and Health. FDA’s preliminary ‘healthy’ labeling rule was released on Sept. 28, 2022, on the first day of the first White House Nutrition Conference since the 1980s.
At that Conference, Ag Secretary Vilsack said: “The National Strategy’s approach is a whole of government approach that involves the entire federal family.” And President Biden said: “We have to give families a tool to keep them healthy. People need to know what they should be eating, and the FDA is using its authority around healthy labeling so you know what to eat.”
In short, the FDA’s role here is to restrict healthy label claims to foods and beverages that meet its criteria and allow them to also use a new FDA ‘healthy’ symbol that is still under development.
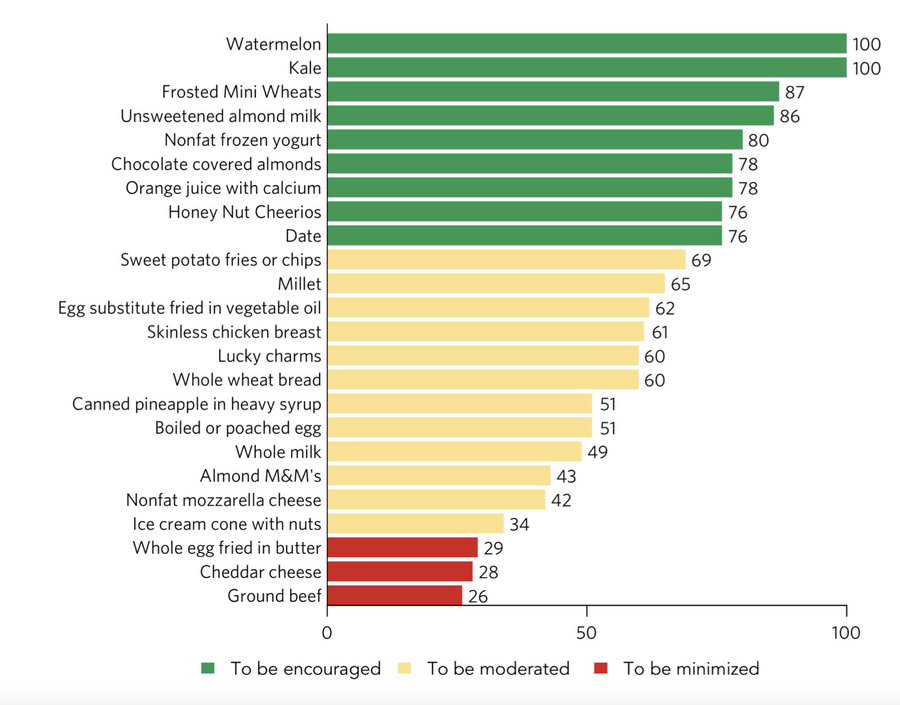
“Nutrient-dense foods that are encouraged by the Dietary Guidelines – vegetables, fruits, whole grains, fat-free and low-fat dairy, lean game meat, seafood, eggs, beans, peas, lentils, nuts, and seeds – with no added ingredients except for water, automatically qualify for the ‘healthy’ claim because of their nutrient profile and positive contribution to an overall healthy diet,” the FDA final rule states.
No surprise that whole milk (3.25% fat) will not qualify, nor will real full fat cheeses, yogurts, and other dairy foods that are not fat-free or low-fat (1%). Natural, unprocessed beef, pork and poultry are off the ‘healthy’ list too.
Specifically, the FDA’s final rule states: “To meet the updated criteria for the ‘healthy’ claim, a food product must: 1) contain a certain amount of food from at least one of the food groups or subgroups (such as fruit, vegetables, grains, fat-free and low-fat dairy and protein foods) as recommended by the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, and 2) meet specific limits for added sugars, saturated fat, and sodium.
The fat and sodium criteria are a double-whammy against most real dairy cheeses. A single 1-oz slice of American, Swiss, or Cheddar won’t make the cut on saturated fat or sodium; even part-skim Mozzarella is slightly over the limit. Furthermore, low-fat, high-protein cottage cheese barely makes the cut on saturated fat, but far exceeds the new limit on sodium. Likewise, a typical yogurt cup only qualifies if it is low-fat or non-fat, and fruited yogurts must steer clear of added sugars.
Dairy can’t win in this labeling scheme unless products are made with virtually no saturated fat and far less sodium. To sell flavorless cardboard and chalk water that fails to deliver key fat-soluble nutrients, products will undergo more ultra-processing, and Americans will consume more artificial sweeteners.
Under dairy products, FDA’s final rule for ‘healthy’ label claims states: 1) Must contain a minimum of 2/3 cup food group equivalent of dairy, which includes soy; and 2) Each serving must have under 2.5 g of added sugar, under 230 mg sodium, and under 2 g saturated fat.
This means even a serving size of exactly 2/3 cup (6 oz) of 2% milk might barely squeak by, and a full cup (8 oz) of 1% or fat-free milk would be – you guessed it – ‘healthy’. Flavoring the fat-free and low-fat milk will not qualify, except by using artificial sweeteners to stay within added sugar limits.
Under protein foods, the FDA is even more restrictive. The only protein foods listed in the ‘healthy’ labeling final rule are: game meat, seafood, eggs, beans, peas, lentils, seeds, nuts, and soy products. Furthermore, these options must meet the criteria of less than 1 g added sugars, less than 230 mg sodium and less than 1 to 2 g saturated fat.
But here’s the good news! This FDA final rule (21 CFR Part 101, RIN 0910-AI13) falls under the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). It’s not likely to sit well with HHS Secretary designate RFK Jr. The rule becomes effective Feb. 25, 2025. The compliance date is three years later, so there is hope of requesting HHS initiate a new rulemaking process under new HHS leadership.
Bottom line is all three of these bad nutrition policies impact consumer health and dairy farm economic health and are rooted in the flawed Dietary Guidelines process.
There is good news on that front in Congress as well. House Ag Committee Chairman GT Thompson included DGA reform and oversight in the farm bill that had passed his Committee in the 2023-24 legislative session. It is critical that this issue be part of the new farm bill that moves forward in the 2025-26 legislative session.
Part II in a future Farmshine will look at the tumultuous 2024 dairy markets and margins spilling over into 2025.
-30-