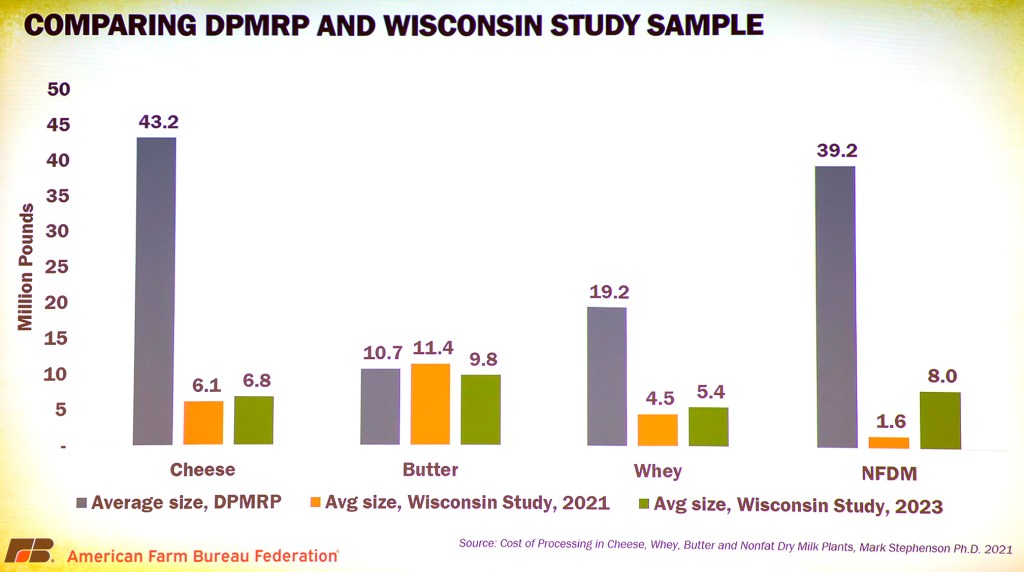
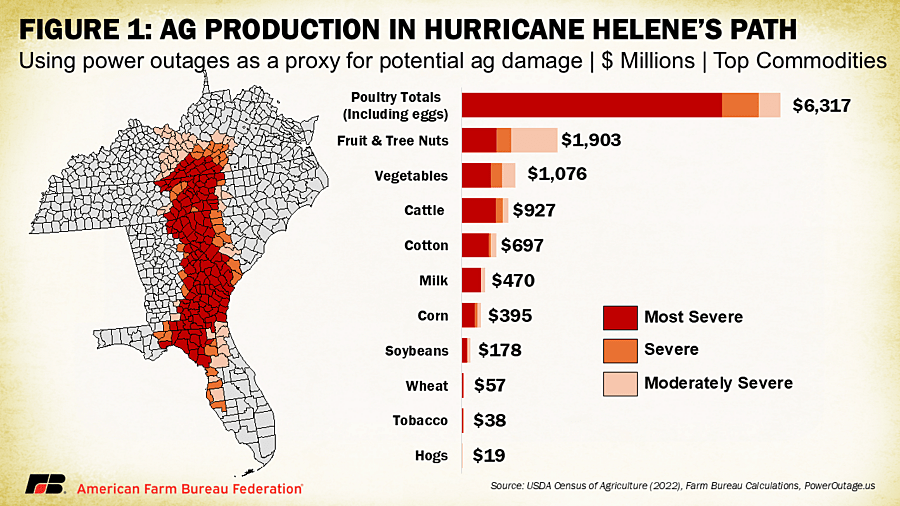
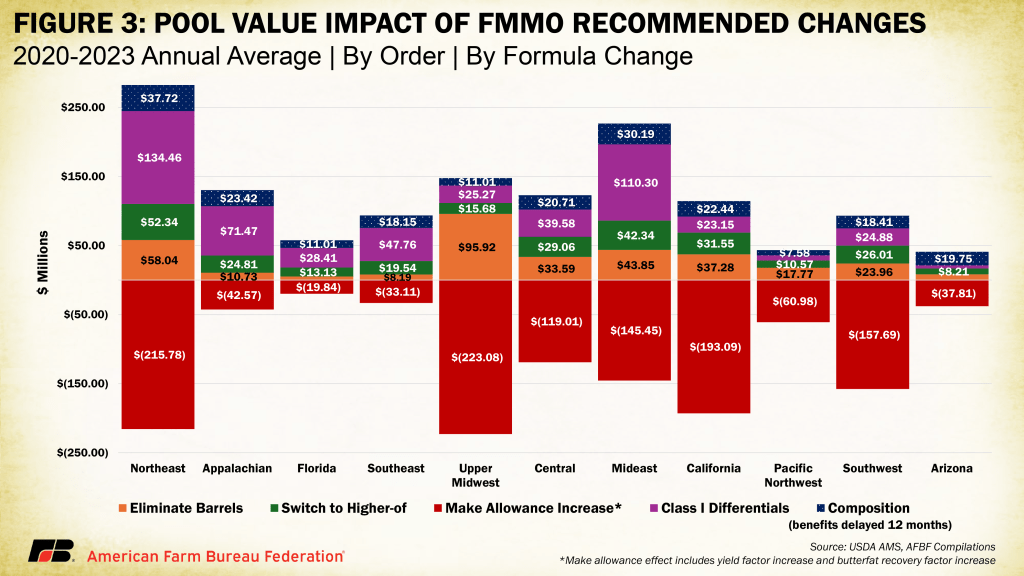
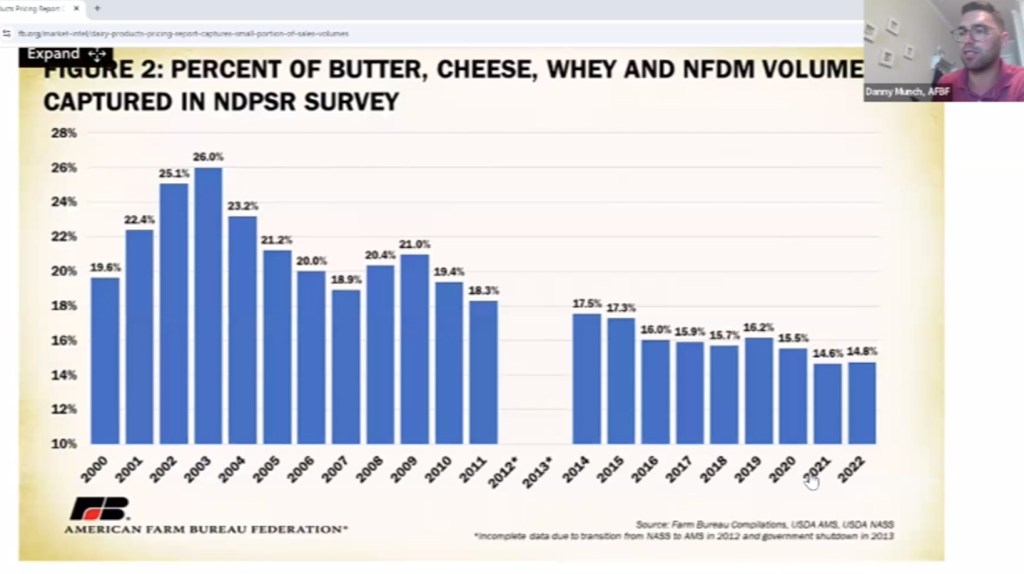
Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee holds final meeting. Draft recommendations include: Reductions in total protein; Less protein from animals, more from plants; Dairy emphasis still low-fat, non-fat; Implementation recommendations include food supply leverage
By Sherry Bunting, Farmshine, October 25, 2024
WASHINGTON, D.C. – This week is National School Lunch Week, and on Oct. 22 while USDA Secretary Tom Vilsack kicked off the so-called “largest federal-led summit in support of healthy school meals” in Las Vegas, the 2025-30 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee (DGAC) met publicly by zoom to gamble away the nutrients children need for the development of their brains, bodies and long-term health.
This was the seventh and final meeting of the DGAC after 22 months of subcommittee meetings and periodic full committee meetings, yielding a draft “scientific report” that is increasingly vegetarian.
Its recommendations to USDA and HHS are to develop 2025-30 Guidelines that significantly decrease the role of nutrient dense animal foods, even though they spent the first hour of the 12-hour, two-day virtual meeting puzzling over how to solve the nutrient deficiencies in their analysis.
The recommendations merge the three current DGA patterns (Vegetarian, Mediterranean and Healthy U.S.) into one dietary pattern with a draft name of “Healthy Flex U.S. Diet.” The flexibility part, according to the DGAC discussion, is the ‘how much’ and ‘how to’, which relies on ‘food pattern modeling’ and more specific strategies on how to replace animal based foods with plant based foods.
The DGAC aims to improve its poor performance on the under-consumed nutrients by “including more nutrient-dense plant-based meal and dietary recommendation options” in its advice for 2025-30 Dietary Guidelines.
The draft advice aims to continue to “emphasize consumption of low-fat or non-fat dairy and unsaturated fats; limit consumption of red or processed meats and foods high in saturated fat; and limit foods like sweetened beverages.”
Some committee members raised the concern that further addressing one problem (fat, salt, and sugar) leads to other problems in other areas (under-consumption of key nutrients, over-consumption of carbohydrates, and impacts on metabolic health).
In fact, a week before the DGAC met, the first ever Change the Dietary Guidelines protest drew hundreds of people to the nation’s capitol — with Nina Teicholz, author of Big Fat Surprise, as emcee. It was organized by Metabolic Revolution with the mission of asking the Administration to “STOP FEEDING US LIES.”

Meanwhile, in the DGAC meeting, at least one member at the end of the first day noted how animal foods, specifically mentioning dairy, have all of these essential nutrients and that the bioavailability of the nutrients is important.
This didn’t make much difference. On the question of saturated fat restrictions, the 2025-30 DGAC doubled-down. These restrictions began with the first edition in 1980, and the quantitative recommendation of “limit saturated fat intake to less than 10% of calories per day starting at age 2 and replacing it with unsaturated fat, particularly poly-unsaturated” began in 2005.
The Committee’s biggest justification was that, “This has been confirmed by several previous DGACs based on the relationship between saturated fat intake and cardiovascular disease risk.” Basically saying it has been previously decided, and “we’re sticking with it.” Essentially, all evidence to the contrary was again ignored.
The Committee stated that only 1 in 5 Americans implement this limitation; so, food replacement strategies, cultural diet pathways, and diet simulations were recommended to show how to get more nutrient density from plant sources. Pre-packaged and pre-portioned implementation strategies and plated combinations of plant-based meals are suggested as ways to ensure nutrients without the fat.
This high-level academic exercise means very little to everyday Americans making choices about food, but it could fundamentally change what is available to choose from — if the “systems science, implementation science, and behavioral science” the DGAC is also recommending pushes diets even more toward highly processed, pre-packaged, pre-portioned options designed by global food giants.
Bottomline: the DGAC will recommend to the USDA and HHS to further reduce animal-based protein consumption and to further increase plant-sourced consumption in the 2025-30 Guidelines, while continuing to limit dairy to non-fat and low-fat options.
For dairy, the DGAC is also recommending that USDA update nutrition composition and dairy reference guides to reflect what they say are ‘improved’ plant-milks, and to use ‘diet simulators’ to show Americans how to be more ‘flexible’ in replacing animal foods with plant foods.
The DGAC also changed the wording of its 2025-30 mission to “reduce the focus on chronic disease risk reduction, to instead focus more on promoting growth and development and improving the healthspan.”
These are key takeaways despite the Committee spending the first hour of the first day stupefied by the analysis showing — uniformly across all socio-economic and cultural demographics — children ages 5-19 had the nutritionally poorest diets in terms of under-consuming key nutrients at this most critical lifestage.
Even when they picked up their Health Equity Lens to look at the data, it was uniformly bad.
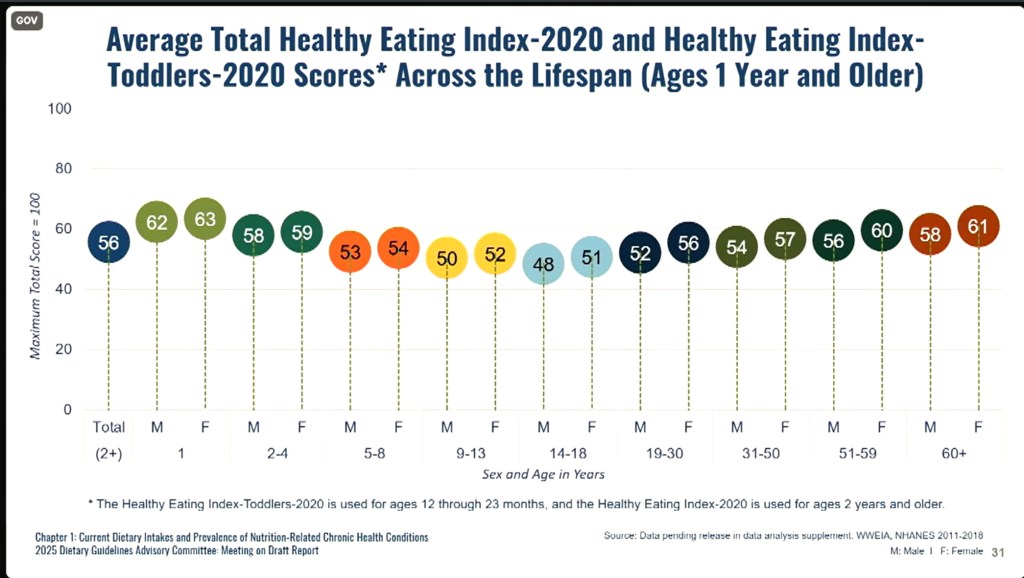
Their interpretation? I will paraphrase: Parents need help understanding how to feed their children.
My interpretation? The Dietary Guidelines are, themselves, the problem because they are used rigidly to formulate the meals that the age 5 to 19 lifestage (kids) are presented with twice a day, five days a week, nine to 12 months of the year – at school! The body will keep snacking until it gets the nutrients it seeks.
“Obesity is a major public health issue, impacting 36% of children ages 2 through 19 years and 41% of adults ages 20 and older,” according to the DGAC.
However, by the end of the two days, the DGAC showed it would stay on the anti-fat path and give USDA and HHS the “expert” advice to double-down on saturated fat restrictions that have prevailed over the years while Americans become less healthy, more obese, with more chronic disease, at ever younger ages. Do they not wonder why this was not the situation pre-Guidelines? So much valuable research on saturated fat and health was again left off the table.

Impacts of the DGAC draft report on Dairy:
1) Dairy’s ‘place’ in the diet remains somewhat intact, but the committee advises things like not referring to soy milk as an “alternative” because it is part of the dairy grouping. They also are questioning if ‘Dairy’ is the right term for the Dairy group. The DGAC also will advise USDA to update nutrient composition and daily reference amounts to reflect the current state of nutrition art in “plant-milks” and to use diet simulations to show Americans how to be more flexible in replacing animal-based with plant-based.
2) Nonfat and low-fat dairy will continue to be the recommendation (3 milk cup equivalents), although they mentioned that there was not enough evidence to make this a strong conclusion for ages 2 through 5. Perhaps this leaves a door open for daycares and WIC to expand to 2% and whole fat milk up to age 5 instead of the current age 2, but schoolchildren are still out of luck. Dairy fat and butter were mentioned as being consumed mostly in processed foods.
3) The Protein category has been flipped on its lid. The DGAC moved beans, peas and lentils from the vegetable category to the protein category and increased the daily quantities for beans, peas, lentils, seeds, soy, nuts, and fish, while reducing the allowance for meat, poultry and eggs. In fact, they will represent this visually by listing first in the protein category the plant sources, followed by fish, then eggs, then poultry, and lastly, red meat. The DGAC pointed to the dairy group as a source of protein that is not in the protein group, so protein level importance in plant-based comparisons can be reduced. (Several Committee members indicated their belief that Americans consume too much protein, so they wanted to show these crossovers differently.)
4) The additional considerations chapter is of particular concern for the future, advising USDA and HHS to: a) Encourage shifts to nutrient-dense plant-based meals; b) Put stricter limits on foods and beverages high in added sugars, sodium, and saturated fat; c) Use sugar limitations to exclude foods from the dietary pattern (with implications for flavored milk and dairy products); d) Make sodium reduction targets mandatory not voluntary (may impact the cheesemaking process for schools and other institutional feeding); e) Avoid referring to soy milk as “alternative”; Research name change for Protein group and determine if ‘Dairy’ is the right term for the Dairy group.
This draft report ends the DGAC’s work. In the coming days, it will be edited to reflect the discussion for submission as final recommendations to USDA and HHS.
A joint team of staff from both Departments will prepare this DGAC Scientific Report for posting at DietaryGuidelines.gov, along with data analysis, food pattern modeling and other supplemental documents.
USDA and HHS will then open a new public comment period.
In 2025, the Secretaries of USDA and HHS (whoever they end up being), along with their joint team, will review the DGAC scientific report and the public comments to develop the actual 2025-30 Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
Expect these DGAs to continue most negatively impacting America’s schoolchildren and elderly in senior centers where meals must follow them.
However, it will have some impact on all of us if the Departments use the DGAC recommendation to implement food system science at the food supply level. We can already see what happens to choices for consumers and markets for farmers when the middlemen decide what can be put on grocery store shelves or in the dairy or meat case.
Not only did we not see a serious effort to address the need for more nutrient dense foods in the dietary pattern, the new pattern will double-down against saturated fat, along with salt and added sugar, and erode protein levels, while continuing to search for the missing nutrition profile of its increasingly vegetarian recommendations.
None of this passes the smell test, and likely not the taste test. Kids eat food not data. Nutrients must pass the tongue to reach the belly. Look for more on that in terms of action next week from the Grassroots Pennsylvania Dairy Advisory Committee and 97 Milk.
***
Additional information:
In its report, The Nutrition Coalition notes: “The collective shift toward emphasizing more plant-based foods has lowered the quality and quantity of protein in our diets. It is time to pause and question whether these changes are endangering health in the U.S., especially among children and the elderly. Still, with plant-based advocates dominating the public comments, plant-based industries and interests lobbying the USDA, and plant-based proponents on the expert committee itself, we may see further reductions of this important macronutrient in the 2025 Dietary Guidelines.”
Nina Teicholz, Ph.D. explains that these draft recommendations “fly in the face of our knowledge that plant proteins are of lower quality than animal proteins. With the exception of soy, all plant proteins lack all the necessary amino acids to make muscle tissue (as well as perform other critical functions in the human body). Reducing the total amount of protein and replacing animal proteins with plant proteins are both harmful changes. These alterations will mean that anyone receiving USDA-funded meals, such as kids consuming school lunches, the women and infant children on the WIC program, and the elderly will receive fewer complete proteins. Also, reductions in meat, dairy and eggs are sure to exacerbate nutritional deficiencies in the guidelines, which currently fail to meet basic targets iron, vitamin D, vitamin E, choline, and folate. The Dietary Guidelines are already deficient in complete proteins. The erosion of protein in the guidelines has been happening for decades, as we wrote about in this post.”
-30-