By Sherry Bunting, Farmshine
WASHINGTON –- USDA officially announced Monday (July 24) the national public hearing to consider proposals seeking to amend the uniform pricing formulas across all 11 Federal Milk Marketing Orders (FMMO). The hearing begins Wednesday, August 23, 2023 at 9:00 a.m. at the 502 East Event Centre, 502 East Carmel Drive, Carmel, Indiana.
Farmers will be able to testify in person at any time, or virtually on Fridays by pre-registering.
Approximately 40 proposals were submitted by 12 organizations and were explained during a webinar in mid-June. Of those, 21 will be considered within the uniform pricing scope of the hearing, according to the USDA notice. Copies of the notice, a list of proposals being considered, guidelines for how to participate, the hearing schedule, and corresponding hearing record can be found and followed on the Hearing Website.
The Class I mover formula will be addressed in the national hearing’s scope, including the proposals from National Milk Producers Federation and American Farm Bureau to go back to the ‘higher of’ method. The change from ‘higher of’ to ‘average of’ was made legislatively in the 2018 farm bill without a hearing.
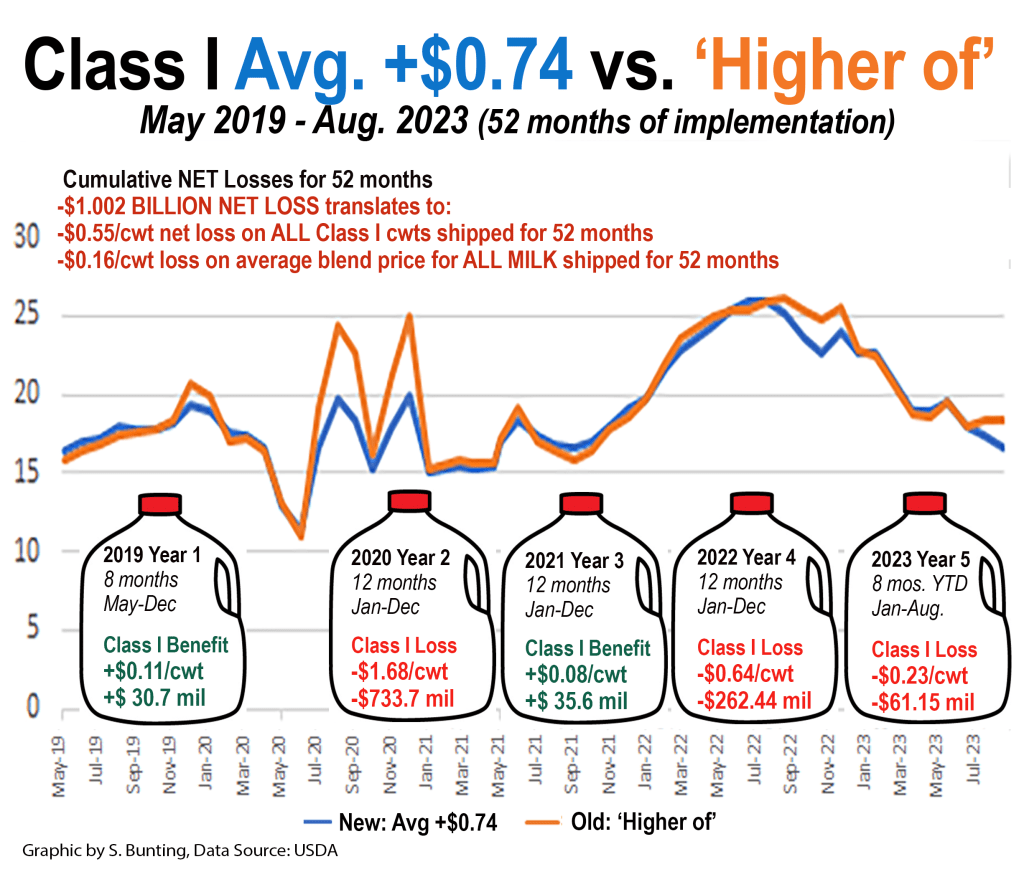
Since USDA implemented the ‘average of’ method in May 2019, net losses from this change are projected to exceed $1 billion after August 2023 milk is paid for in September.
On July 19, USDA announced the August advance Class I price mover at $16.62. If the previous ‘higher of’ method had been used, the Class I base price would have been $18.29. That’s a $1.67 per hundredweight loss on all Class I milk next month. July’s Class I mover was also calculated substantially lower (by $1.02) using the ‘average of’ vs. the ‘higher of.’ These losses will impact August and September milk checks for July and August milk.
Around 28% of all milk produced in the U.S. is Class I fluid use, so farmers stand to lose an additional 47 cents per hundredweight on all of the milk they market in August and 29 cents on all the milk they market in July — just from this formula change. This is on top of the market declines in the class and component prices. The loss to blended prices will be greater in some Federal Orders and less in others, and this does not include the impacts from de-pooling of higher-value Class IV milk.
The impact of the two-week Class I advance pricing factors is compounded by the ‘average of’ method, which is quite notable for July and August. Cheese and whey were in a tailspin lower; however, on the very next day after the August Class I base price mover had been averaged and locked-in on July 1-15 pricing factors, the dairy product markets began a huge rally, with cheese gaining nearly 40 cents in 8 trading sessions. This boosts the other class and component values much higher for the latter half of the month.
Over the 52 months of its implementation, the ‘average of’ formula has effectively removed an estimated 55 cents per hundredweight from farmer payment for all Class I milk, according to USDA data. On a blended uniform price, this comes out to a national average loss of 16-cents on every hundredweight of all milk used in all classes of products shipped from May 2019 through August 2023. That is like paying another checkoff for 52 months.
Among the other proposals included in the national hearing is the American Farm Bureau (AFBF) Class I and II proposal that seeks return to the ‘higher of’ with additional adjustments such as eliminating the two-week ‘advanced’ pricing.
IDFA’s Class I proposal seeks to keep the ‘average of’ and use either the current 74-cent-adjuster or a ‘rolling adjuster’ based on a calculated difference over 24 months, whichever is higher.
Milk Innovation Group’s (MIG) proposal seeks to keep the ‘average of’ but change the ‘adjuster’ monthly via a 24-month look-back with a 12-month lag.
Two Edge Cooperative proposals are included, one being a Class III-plus formula. The other would use the ‘higher of,’ but would base it on end-of-month four-week announced class and component prices instead of the two-week prior month advance pricing.
The hearing docket also contains four proposals on Class I differentials, including NMPF’s proposal to increase them in all locations by varying amounts as well as MIG’s proposal to lower them across the board by $1.60.
Two proposals from NMPF and National All Jersey will be heard to update milk component factors.
Six proposals will be heard on Class III and IV pricing formulas. Three are separate proposals from NMPF, IDFA and Wisconsin Cheesemakers to update processor credits, known as ‘make allowances,’ as well as three from Select Milk Producers on butterfat recovery, farm to plant shrink and nonfat solids yield.
In addition, the hearing scope includes four proposals on how dairy commodity products are surveyed, including NMPF’s proposal to remove 500-lb barrel cheese from the weekly survey, AFBF’s proposal to add bulk 640-lb block cheese and unsalted bulk butter, while California Dairy Campaign’s proposal would add mozzarella.
Dairy farmers can testify in-person at any time during the hearing, or virtually on Fridays. Beginning Fri., Sept. 1 and for each Friday thereafter until the hearing concludes, dairy farmers may testify virtually in 15-minute time slots beginning at Noon ET. There will be 10 slots for virtual testimony each Friday.
To be included, farmers must pre-register. The pre-registration for each Friday’s time slots will be available starting Monday of the same week at the USDA Hearing Website. For example, the link to testify on Fri., Sept. 1 will be available on Mon., Aug. 28. To submit exhibits for the record, email them to FMMOHearing@usda.gov by 8:00 a.m. ET on the day of testimony.
Those participating in the hearing in person should notify a USDA official upon arrival at the hearing. For additional information, contact Erin Taylor, Director, Order Formulation and Enforcement Division, USDA/AMS/Dairy Program at Erin.Taylor@usda.gov.

